Merchant Accounts Are a Necessity for Accepting Credit Cards. But, What is a Merchant Account & What Does it Do?
A merchant account refers to a type of business bank account. It’s nothing like a consumer checking or savings account, though.
They’re only available to businesses, and they’re a crucial part of the payment process. In short, your merchant account lets you accept and process electronic credit card payments. That’s why you need to work to protect your account at all costs.
Recommended reading
- 7 Common Reasons Why Issuer Declines Happen
- Merchant Identification Number: How to Find Your Merchant ID
- My Bank Account is Under Investigation? What’s Going On?!
- VAR Sheets: Get All Your Documents Ready in 4 Basic Steps
- Internet Processing: Understanding the eCommerce Process
- Issuer vs Acquirer: What’s the Difference?
What is a Merchant Account?
- Merchant Account
A merchant account is a bank account that is used to temporarily hold funds from payment card transactions after processing, until the money can be transferred to the business’s permanent business bank account.
[noun]/mur • chnt • ə • kown • t/Let’s start from the beginning, and explain, in simple terms: What is a merchant account? What does it do?
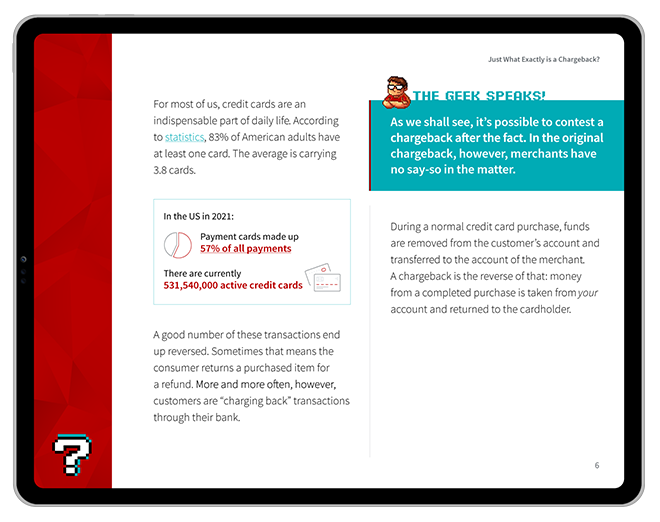
You can think of a merchant account as a temporary holding place for the funds involved in an eCommerce transaction. Paying with a card isn’t a direct transfer from buyer to seller. With credit and debit sales, the seller basically gets an IOU; the buyer is essentially saying “My bank will give you the money I owe for this transaction.” This is either confirmed — or denied — through the authorization process.
Learn more about authorizationIn theory, the bank that issued the payment card could initiate a transfer immediately. They don’t, though, because the automated clearinghouse process is not instantaneous. Before the bank transfers the funds, they want to check the buyer’s account and make sure they have enough available funds or credit to cover the cost of the transaction.
In a sense, merchant accounts serve as another failsafe in that process. Instead of sending the money directly to your commercial bank account, the issuer releases the funds to your acquirer, who deposits them into your merchant account. The funds are held there securely until the transaction is approved and cleared. Finally, the money can be released to your regular commercial bank account (a process called “funding”).
This process often takes 3-5 business days. That said, some acquirers do offer next-day account funding.
So, that addresses the question of what is a merchant account. Next, we’ll see why you actually need one.
Why Do I Need a Merchant Account?
The simple answer is “to receive payment for sales.”
You must have some type of merchant account before you can accept credit card transactions. It’s not just a formality, though; there are several benefits for you in this process. There are options you can consider, as we’ll examine later. First, though, let's see what is a merchant account going to offer you:
Different Types of Merchant Accounts
Merchant accounts are often meant to correspond to your business model. For example:
Brick-&-Mortar Retailers
Retail merchant accounts work for sellers who primarily operate out of physical locations. In-person sales are considered less risky than electronic transactions, so account providers may require that a certain percentage of the merchant’s transactions come from a physical card reader.eCommerce Merchants
Things are more complicated for online sellers. Card brands like Visa and Mastercard require dedicated merchant accounts, meaning you will need a separate internet merchant account for each card brand you accept. An online payment gateway service will also be necessary for selling through online channels.B2B Merchants
Providing goods or services to other businesses (or government entities) means you may need a specialized business-to-business merchant account. Since these types of organizations are considered less risky, you can often qualify for lower processing rates.Mobile Merchants
Some merchants work in different locations and, as a result, need to accept credit card payments “on the go.” Mobile accounts use an inexpensive card reader that integrates with a phone or tablet, enabling buyers to swipe a card from anywhere.Telephone/ Mail-Order Merchants
You need a specific type of account to accept payments by phone or through the mail. For convenience, many providers offer these options as add-ons to other types of merchant accounts.Aggregator Merchants
Merchant aggregators are organizations with their own merchant identification number (MID). For a price, other sellers can become “sub-merchants,” sharing the aggregator’s merchant account. This may work for retailers who are small or mid-sized, are considered high-risk but don’t want to pay for a high-risk merchant account, and don’t offer extra services like loyalty rewards or subscriptions.
How Much Does a Merchant Account Cost?
Next, let’s examine what is a merchant account going to cost you.
Merchant account fees vary based on the volume of card transactions processed, with the highest expense generally being the credit card processing fees charged by the payment processor.
So, what is a merchant account going to cost you on a per-transaction basis? That depends. There are three main pricing models used by merchant account providers:
Of course, there are other costs beyond per-transaction fees. You may be expected to pay:
| Fee | Payable | For |
| Setup fee | One-time, upfront | Account setup |
| Ongoing fee | Monthly or annually, depending on contract | Ongoing provider services |
| Monthly minimum fee | Monthly, if required | Charges added to make up a shortage to minimum monthly processing fees |
| Batch fee | Daily, after transactions are batched and transmitted | Processing fee |
| PCI compliance fee/PCI non-compliance fee | Monthly, annually, or included in ongoing fee | Cost for compliance services or penalty for non-compliance |
| Early termination fee | End of contract, if applicable | Penalty for ending a long-term contract early |
| Statement fee | As applicable | Admin fee for mailing paper statements |
| Chargeback fee | Whenever a customer successfully files a chargeback | Admin fees for processing the dispute |
How to Obtain a Merchant Account
Opening a merchant account can be work-intensive. That said, the steps are not difficult to follow. So, what is a merchant account requirement list?
You will need a business license, a business (commercial) account, and possibly an employer identification number (EIN). A valid government-issued photo ID will also be required. Some of the things providers may want to know include:
Before even applying, you should get cost estimates from multiple providers. Ask for detailed pricing structures, contract lengths, security measures, and support options.
Once the possibilities have been narrowed down, it’s time to fill out applications. This involves presenting all the business information and supporting documents you’ve gathered. The account provider will look over these documents, and use them to determine eligibility (as well as how much it will cost you.)
Because merchant accounts represent a risk for both the account provider and the acquiring bank, the provider will underwrite your business before accepting you. Established businesses typically won’t have much trouble with the underwriting process, but account providers may be more hesitant to take on the risk of a new business.
If everything goes well and your business is approved, you should be able to begin processing right away.
Other Options: What is a Merchant Account Alternative?
As mentioned earlier, merchant accounts are required in order to accept credit cards. That said, the merchant account does not necessarily need to be directly tied to that one merchant.
We’ve already talked about aggregator accounts, where several companies share the merchant account of one payment service provider (PSP). An independent sales organization (ISO) does much the same thing. But, instead of having multiple sub-merchants, it serves as a type of proxy for a single large client.
There are numerous advantages here. In some cases, for example, a seller may not even be able to get a merchant account due to operating in a high-risk vertical. Instead, they opt to use an ISO; one which probably has a squeaky-clean reputation with the bank.
Next, we have payment facilitators (or “PatFacs”) like PayPal or Square. These can perform the services of a merchant account, even if they are not technically merchant account providers (MSPs). PayPal, for example, acts as a gateway and processor. However, it lets you hold transaction funds in your own account, instead of a separate merchant account.
While this option may work for new or very small businesses, the service isn’t really built for scalability. Also, PayPal’s transaction fees tend to be higher than those of a traditional merchant account, and the service may not be as robust or customizable as a business needs.
The biggest difference between an MSP and a PayFac is long-term functionality. Customer support has been an ongoing, often-reported issue. Small business owners have lodged complaints that range from frozen funds to accounts suddenly being terminated over something as innocuous as an increase in average ticket size.
What About Chargebacks?
What is a merchant account holder’s typical exposure to chargebacks?
Any merchant accepting credit cards is vulnerable to chargebacks (forced payment reversals). A chargeback is issued when a cardholder disputes a charge on their card and the issuing bank refunds the customer’s money.
If your business is high-risk or you deal with excessive chargebacks, keeping your merchant account can be more difficult than getting it in the first place. Card networks like Visa and Mastercard set firm chargeback thresholds, limiting the number of chargebacks you may receive in a set period of time. If you breach these thresholds — or even come close, in some cases — your acquirer may terminate your merchant account.
MSPs, banks, processors, card networks — all organizations involved in processing credit cards hate chargebacks. That’s why many merchant account providers offer fraud management tools and chargeback protection software. It’s helpful, but it may not be enough.
True chargeback management and risk mitigation require a more comprehensive approach. If you’d like to know more, contact Chargebacks911® today.
FAQs
What is a merchant account?
A merchant account is a specific type of bank account that allows merchants to accept payment cards for purchases.
How do merchant accounts work?
A merchant account at an acquiring bank is more or less a depository account. It’s a secure place for customer payments to sit while the bank checks to make sure the customer has enough money in their account to make payment. Once the transaction is settled, the funds will be transferred to the seller’s business account.
Is a merchant account the same as a bank account?
No. They are two entirely different things. Bank accounts typically hold any amount of money forever, or until it is used. Merchant accounts only temporarily hold funds from payment card transactions, and only until the transaction is settled.
How do you qualify for a merchant account?
Merchant accounts are only issued to businesses, so you’ll need a business license, a business bank account, and a government-issued employer identification number (EIN).
Can an individual get a merchant account?
Merchant accounts are only open to businesses. The closest thing to an individual merchant account is one used by a sole proprietorship.
How much does it cost to open a merchant account?
Not counting the funds needed to open a business checking account and the cost of a card reader or point-of-sale (POS) system, the account provider will often charge a one-time set-up fee. The amount will vary according to the acquirer.