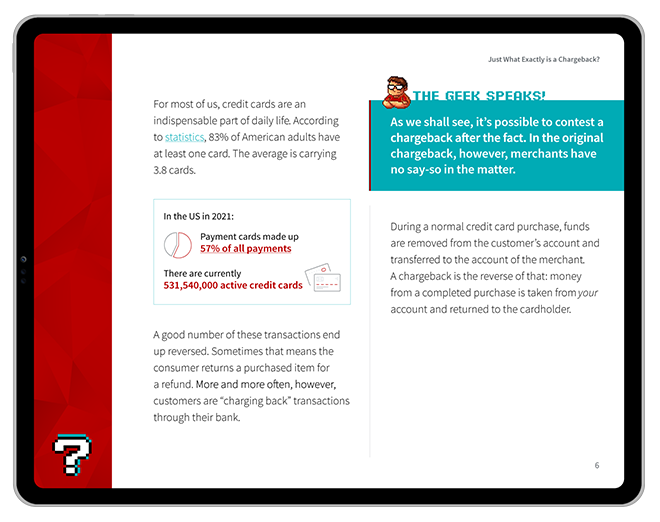
In short: a QR code payment can refer to any monetary exchange made by scanning a QR code from a mobile app. What's that mean, though? How does it work?
A QR code (or “quick response code”) is a scannable technology featuring a 2D barcode that is readable by a camera on a smartphone or other device. Although it may appear similar to the linear barcodes we see in the grocery store, QR codes contain 4 distinct advantages over their predecessors.
These QR codes:
- Can contain a higher volume of data storage
- Are scannable from photos or screens
- Can still be readable even when damaged
- Feature complex encryption
QR codes were first invented in 1994 by a Japanese firm for use in the auto industry. The idea was to allow faster and more accurate component scanning compared to existing barcode systems. In response to that need, a single QR code can hold up to 7,000 unique characters and scan up to ten times faster than a traditional barcode.
At the dawn of the smartphone age, some saw the QR code as a potential medium for exchanging all data types. After all, any device with a camera can scan them. However, it wasn’t long before these codes fell out of favor and were largely written off as a failed tech concept…at least, so everyone thought. Fast-forward to the present, and QR codes are making a comeback as a valuable asset in the payments space.
Recommended reading
- What is EMV Bypass Cloning? Are Chip Cards Still Secure?
- Dispute Apple Pay Transaction: How Does The Process Work?
- Terminal ID Number (TID): What is it? What Does it Do?
- How EMV Chip Cards Work: Pros, Cons, Data Points & More
- The AI Gap: Banks’ Slow Adoption Creates Chances for Fraud
- Point of Sale Systems: How to Get More From Your POS Machine
What is a QR Code Payment?
Like we mentioned above, a QR code payment is a contactless alternative payment method made by one user scanning a QR code from a mobile app.
QR codes can be used as an in-app payment method for branded apps. It can also serve as an alternative to a conventional credit card payment at the point of sale using a payment terminal. Both of these methods are forms of electronic funds transfers.
The ability to process QR codes was a leap forward in payments technology. QR codes can allow you to accept payments without an up-front investment in a lot of the infrastructure traditionally associated with electronic payments.
You don’t need to secure a terminal, a merchant account, or a card reader to accept payments. You can also work outside of card networks like Visa and Mastercard. To process a QR code, all you technically need is a smartphone or tablet with a built-in camera, or another barcode reader capable of scanning QR codes.
Also, because it is so versatile and sleek, it is extremely popular with consumers worldwide. Thus, despite the technology’s formerly lackluster performance in the US, many global companies are beginning to catch on.
How Do QR Code Payments Work?
When scanned, the lines and shapes in the QR code pattern matrix are decoded by the software enabled on your smartphone or device. That data is then converted into a complex string of characters that your phone will read as a command to either open a link, verify geolocation, or confirm payment information.
You can process QR payments through any of the following methods:
Why didn’t this catch on earlier? Perhaps one of the reasons QR codes failed to impress initially was due to the sluggishness of first-generation smartphones and wireless networks. Nowadays, though, smartphones are exponentially more powerful. Responses take nanoseconds, rather than minutes.
That said, many smartphone users are still hesitant to use apps to make purchases on their cellphones. Some find the time it takes to open an app and scan codes a pain. For others, it’s a lingering (if misguided) sense of anxiety about security of the technology.
Where Are QR Payments Currently Being Used?
China seems to be where adoption of QR code payments is strongest. In fact, making payments via a QR-enable device is the preferred transaction method in China, from luxury department stores to street vendors, all but leaving credit and debit cards in the dust.
China’s mobile payments adoption is leading the industry with a penetration rate of nearly 41%, which is 44% higher than any other country in the world. Most of these transactions occurred via mobile payment apps like Alipay and WeChat.
As China shifts its focus to regulating risk management in the mobile payment market, many Central- and East-Asian countries are following their lead. For instance, merchants in Vietnam, South Korea, and India have also embraced QR payments. Mobile QR codes have become the norm in much of this region.
This is seen as a move to both modernize and diversify in a fast-growing economy. Sill, even beyond that region, the United Kingdom, Germany, and Portugal have joined the US in broadening their contactless payment interests as well.
Top 5 QR Code Payment Providers
As you might have guessed, the main benefits of QR payment technology are speed, security, and contactless convenience. How can you get in on this growing trend, though?
With modernization and consumer demand in mind, if you’re a merchant seeking to diversify your mobile payment options with QR code technology, there are several ways you can go about it. Remember, the payment services you require will rely heavily on your individual needs and industry. For instance, some QR code payment options require a POS to take payments, while others don’t. Depending on your needs, you may only require a tablet or smartphone to accept QR codes.
So now, let’s discuss a few US-based payment processors that are driving QR code functionality.
Square
“Best for Small Businesses”
Square is by far the most versatile cloud-based POS system on the market today, and is also one the most recognizable. Merchants can sell in-person, online, over the phone, or out in the field. Square offers magnetic stripe, chip, and contactless card readers for accepting payments via debit and credit cards, Google Pay, Apple Pay, and QR code payments.
Pros:
- $0 monthly fee
- Versatile QR code payments
- Works in any industry
- Apps not required by customers
Clover
“Best for Brick-and-Mortar”
Clover's Android-based POS system features several hardware options and is very retail-friendly. It’s great for merchants with a small, but permanent retail outlet. A popular cloud-based POS system among small retailers and coffee shops, Clover is QR code payment-enabled and features various options for merchants.
Pros:
- All-in-one POS
- Month-to-month pricing
- Apple Pay QR code payments for cafes
- Venmo & PayPal QR code payments for general business
Cons:
- Higher QR code payment fees for Clover Dining (3.5% + $0.10)
- Customers must have Apple Pay, Venmo, or PayPal for QR code payment
Toast
“Best for Restaurants”
An Android POS system, Toast was designed expressly for restaurants. Aside from a plethora of online ordering and delivery options, Toast makes it easy for restaurant patrons to order and pay using built-in QR payment codes.
Pros:
- Does not require third-party apps
- Digital ordering and reservation features
Cons:
- QR code payment fees higher than competitors (3.5% + $0.15 per transaction)
- Requires a long-term contract
Venmo
“Best for QR Beginners”
Venmo, owned by PayPal, is a trusted name in peer-to-peer payment technology. Venmo introduced QR code payments in 2017. The good news is you don’t need a POS to use it; just a mobile device or even just a username will suffice.
Pros:
- Make in-person payments to anyone
- Doesn’t require a POS system
- QR code payment processing as low as 1.9% + $0.10 per transaction
- Can integrate with Clover and PayPal Here
Cons:
- Customer must have the Venmo app
- Limited POS integration
PayPal Zettle
“Best for Multichannel Merchants”
If the goal is to find a POS you can run on the go, and in separate locations, PayPal Zettle (and PayPal Here) accepts in-person and Venmo QR code payments. This would enable your business to take PayPal payments in-person or online and also sync these sales with any payments you receive on a mobile merchant basis. PayPal Here is a convenient and easy-to-use free POS, with no monthly software fee. You only pay a flat 2.7% fee on all transactions, including credit and QR code payments.
Pros:
- Accept PayPal and Venmo payments in-person
- Low QR code payment fees (2.7%)
- $0 monthly fee
- Automatically syncs with PayPal Business account
Cons:
- Not ideal for larger businesses
- Customers must have PayPal or Venmo for QR payments
Are There Disadvantages to QR Code Payment Acceptance?
QR payments promote—and often deliver—on the promise to prevent instances of transactional fraud. That said, it’s still not a complete solution.
A fraudster can replicate or counterfeit QR Code data to defraud merchants during a transaction. Additionally, QR payments are not always effective at preventing chargebacks, depending on the technology involved. Given that chargebacks are a growing concern for two-thirds of merchants, this is definitely worth consideration.
The same applies to post-transaction threats like friendly fraud. Friendly fraud and return fraud occur after the payment has been finalized, and are therefore not something technology can account for. After all, post-transactional fraud like this is committed by otherwise legitimate customers…not your average cybercriminal.
So, how do you meet the rising demand for QR Code payments and keep your business safe from chargebacks and post-transactional fraud? The answer is to adopt tools and technology to prevent fraud, and take steps to manage chargebacks in the short- and long-term.