How Should Regulators Approach the Fintech Space? Is Open Banking the Secret?
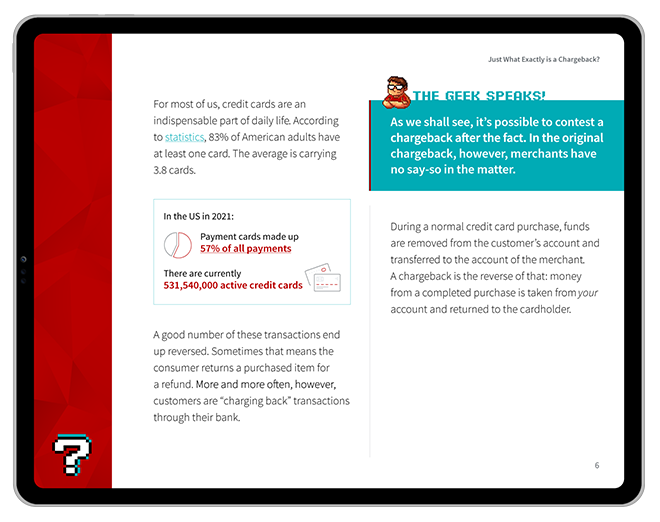
For a long time, regulators tended to focus their attention on traditional banking systems, while fintech companies operated with relatively limited oversight. This was largely due to the fact that legacy financial rules didn't quite match the unique characteristics of these tech-driven financial companies.
Things have shifted now, though. In most markets, big-time financial watchdogs have fintech firms on their radar. These agencies have even tweaked some rules to better suit the particular needs of the fintech scene.
Regulating fintech firms isn't a walk in the park. In many ways, it's actually more complex than overseeing conventional financial institutions.
The fintech space needs regulation. The real question is what regulatory measure is the best fit for fintech?
Recommended reading
- How to Use a Contactless ATM & Where to Find Enabled Devices
- Terminal ID Number (TID): What is it? What Does it Do?
- What is EMV Bypass Cloning? Are Chip Cards Still Secure?
- Dispute Apple Pay Transaction: How Does The Process Work?
- Visa+: Get the Most Out of Digital Wallets With This Tool
- Mastercard Installments: How Mastercard BNPL Works
Why is Regulation Necessary?
Over the years, regulations have matured to shield banks, their clients, and the broader economy from financial wrongdoing. Rules around Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know-Your-Customer (KYC) procedures frequently get tune-ups to stay ahead of evolving scams and criminal tactics.
Fintech encompasses a variety of companies offering banking services, verifying customers, and facilitating transactions. Given the sensitivity of those operations, it's crucial to maintain the same rigorous safety measures that big banks do.
Regulation does more than just protect consumers. When properly devised and implemented, regulation:
In other words, without guidelines, fintech companies would find it tough — maybe even unfeasible — to make a big splash in the world of financial services.
Who Currently Regulates Fintech?
The body responsible for crafting and enforcing fintech regulations varies by country or region.
In the UK, for instance, regulatory compliance demands are very stringent. Fintech entities must align their operations with standards set by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA). Additionally, compliance with the Proceeds of Crime Act of 2002 is a statutory requirement.
Here in the United States, the regulatory landscape for fintech is multifaceted. Various agencies oversee different aspects of the sector. For instance:
Ambitious fintechs planning to scale, whether by acquiring a full banking license or leveraging an e-money license, will encounter regulatory challenges. However, these should be comparable to those of established financial institutions. At least, that’s how it should work in theory.
Is More Regulation Needed?
A recent report from the US Treasury Department reveals that, while the banking sector is becoming more centralized, fintech firms are shaking things up by introducing new business models and increasing competition in key consumer finance areas. That sounds good, but it's not all rosy.
The rise of fintech brings with it a set of challenges, including consumer protection risks and concerns over data privacy and regulatory compliance. To safeguard consumers and promote healthy competition in these fast-evolving markets, the report advises stronger oversight of non-bank entities in the consumer finance sector, among other recommendations.
It's crucial for regions to offer a transparent and consistently applied set of rules for the relationship between traditional banks and fintech firms. This is vital to ensure the integrity, safety, and reliability of the financial markets. For instance, any consumer financial services facilitated through a partnership between a fintech and an Insured Depository Institution (IDI) should comply with all applicable laws, standards, and regulations that govern the IDI.
Which Regulatory Method is Best for Fintech?
So, which is the best regulatory pathway for fintech? Let's look at three models that are currently up for debate:
The Role of Inclusion in Open Banking
As we’ve discussed frequently on this blog, open banking could be the key to striking a balance between scalability and regulation. If we consider inclusion as a preferable approach to fintech regulation, financial firms and regulators can benefit in several ways.
Open banking has the potential to open up a wealth of opportunities in the financial sector. By granting third-party financial service providers access to data from banks via Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), open banking is setting the stage for a host of personalized financial products. Think along the lines of custom-tailored budget apps, innovative loan offerings, and even unique investment avenues.
Not only does open banking pave the way for more innovative products, but it also stirs up some healthy competition among banks and other financial institutions. The result? Better rates and more consumer-friendly products, thanks to collaborations between these institutions and third-party developers.
Open banking has a particularly transformative role to play in financial inclusion. At scale, it would:
#1 | Boost Financial Literacy
Open banking offers a platform for educating the public about managing their finances. Third-party providers can offer educational resources that demystify complex financial concepts and inform people about the array of financial products at their disposal.
#2 | Expand Credit Access
With open banking, financial institutions can gather richer, more nuanced data about borrowers. This includes transaction histories and varied income streams, allowing lenders to make more educated decisions. This is a win for underserved communities that traditionally face barriers to credit, like those without an established credit history or those with low credit scores.
#3 | Pioneer Financial Products
Open banking also gives fintech companies the data they need to develop groundbreaking financial products, particularly for those who are under-banked. For example, they could offer loans with more forgiving interest rates and flexible repayment schedules, tailored to those who might not have easy access to traditional financial services.
#4 | Slash Transaction Costs
Collaboration between financial institutions and third-party providers could mean more economical and quicker payment options for consumers. Think mobile payments or digital wallets that could particularly benefit those who don't have ready access to standard banking services.
#5 | Streamline Financial Management
Third-party service providers can develop budgeting tools that sift through a user's financial data to offer insightful spending analyses and savings tips. These tools can guide people in setting up a budget, monitoring their expenses, and spotting opportunities to save.
The Future is Uncertain, but Promising
Ultimately, it’s too early to say which regulatory method will pave the way. Still, open banking holds immense promise.
It could enhance financial inclusion and empower individuals and businesses to manage their money better. It could make individuals more able to secure credit and engage more fully in the digital economy.
This financial landscape will continue. to evolve. As it does, the key will be to balance innovation and competition while safeguarding consumer privacy and security.