How to Use a Contactless ATM & Where to Find Contactless-Enabled Devices
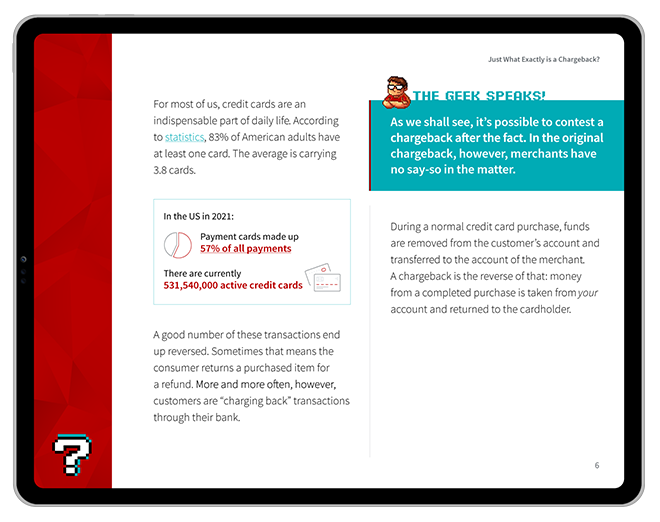
Smartphones today provide individuals with access to virtually anything they need. Banking is no exception.
We have digital wallets like Apple Pay, as well as other mobile payment tools like Venmo and Cash App. With all these technologies on the market, paying for items using a phone has become a standard, convenient, and effortless option.
But what about accessing cash from an ATM? Yes, even that can now be done by phone. Continue reading to discover how cardless ATMs function and provide users with this modern convenience.
Recommended reading
- What is EMV Bypass Cloning? Are Chip Cards Still Secure?
- Dispute Apple Pay Transaction: How Does The Process Work?
- Terminal ID Number (TID): What is it? What Does it Do?
- What is EMV Technology? Definition, Uses, Examples, & More
- Visa Installments: How it Works, Benefits, & Implementation
- dCVV2: How do Cards With Dynamic CVV Codes Work?
How Contactless ATMs Work
Contactless ATMs, also known as cardless ATMs, are devices that let individuals access their accounts and withdraw money without the need for a physical card.
To use the cardless option at an ATM, users typically require their financial institution's app or their card information stored in a digital wallet. A cardless option can then be selected to authenticate the transaction and obtain cash.
Cardless ATMs offer a convenient and innovative way for individuals to access their accounts and withdraw cash without needing a physical debit or credit card. These ATMs leverage new technologies to provide a seamless and secure user experience.
Here's a more detailed explanation of the three primary technologies enabling cardless ATMs:
These technologies, individually or combined, ensure that cardless ATMs offer a secure and convenient alternative to traditional ATMs. Users can benefit from the added flexibility and efficiency of cardless transactions, while financial institutions can leverage these technologies to enhance customer satisfaction and reduce the risk of fraud.
Are Any Financial Institutions Using Contactless ATMs?
Yes. Several prominent banks have incorporated cardless ATMs into their networks, embracing this innovative technology to enhance user convenience and security. A few of the highest-profile of these institutions include:

Additionally, financial institutions that are part of the Co-Op ATM Network may also offer access to cardless ATMs. This includes more than 30,000 machines across all fifty states, plus nine other countries. The same applies for Mastercard-branded ATMs that permit fee-free withdrawals.
To determine whether a particular ATM supports cardless transactions, individuals can look for a contactless tap symbol or logo displayed on the ATM.
How to Use a Contactless ATM
Using a contactless ATM is a simple and convenient process. While the specific features and functions may vary depending on the bank or the ATM model, the steps below outline the general process:
Step #1 | Locate Contactless ATM
First, users will need to find an ATM that supports contactless transactions. These ATMs are usually marked with a contactless symbol or logo, or they can be located using a bank's mobile app or website.
Step #2 | Prepare Device
Ensure the compatible device has the necessary mobile banking app or digital wallet installed. This app should be linked to the user’s bank account or debit card. Ensure the device has sufficient battery life and has NFC (Near Field Communication) enabled if required.
Step #3 | Initiate Transaction
Follow on-screen instructions and prompts. Depending on the ATM model, users may need to tap their smartphone or device on the contactless symbol or hold it close to the designated reader. Alternatively, some ATMs may require users to open their mobile banking app or digital wallet to select the option to withdraw cash or conduct other transactions.
Step #4 | Authenticate Identity
Contactless ATMs may use advanced 2FA authentication methods such as biometrics (like fingerprint or facial recognition). Or, they may use device-based authentication methods, like a one-time code sent via SMS or push notification. Follow the instructions provided to verify identity.
Step #5 | Complete Transaction
After verification, users should follow the on-screen prompts to complete the transaction as with any conventional ATM. For example, if withdrawing cash, the user should select the account and enter the amount to withdraw, then confirm the selection and wait for the ATM to dispense the cash.
Step #6 | Collect Cash & Receipt (if Applicable)
Some contactless ATMs offer the option to receive a digital receipt via email or text message, while others may still print a physical receipt. Collect the cash and/or receipt, if desired.
Step #7 | End Session
Make sure to properly end the session on the ATM screen or the mobile banking app, as instructed. This step ensures personal information and transaction details are secure.
Some ATMs might offer additional services. For instance, users may be able to top-up a prepaid card, deposit a check, or make foreign currency withdrawals. Others may have a more limited scope, though, offering simple account inquiries and withdrawals.
General Advantages of Contactless ATMs
Aside from the obvious “cool factor” that new technologies possess, there are many practical reasons to use contactless ATMs. While this list is by no means exhaustive, here are a few key reasons why someone might prefer a contactless ATM:
Enhanced Hygiene
Since contactless ATMs do not require touching the machine's surface or keypad, the risk of transmitting germs and viruses is significantly reduced. This is particularly important during a pandemic, or even just during the annual flu season.Improved Security
Contactless ATMs use advanced authentication methods, such as biometrics or smartphone-based authentication. This can help minimize the risk of fraud or theft due to card skimming and shoulder surfing.Faster Transactions
Contactless transactions are generally quicker than traditional ATM transactions since they don't require inserting a card or entering a PIN. This can save time, especially during peak hours, or for users who frequently withdraw cash.Enhanced Accessibility
Contactless ATMs can be more accessible for individuals with disabilities, as they may not need to navigate physical buttons or input devices.Reduced Wear & Tear
Contactless transactions reduce the physical wear and tear on both cards and ATMs, potentially increasing the lifespan of both.Integration With Digital Wallets
Contactless ATMs can be compatible with digital wallets and mobile banking apps, allowing users to manage their finances more seamlessly and access multiple accounts through one device.Eco-Friendliness
By reducing the need for physical receipts and using less energy for card processing, contactless ATMs can be considered more environmentally friendly.General Disadvantages of Contactless ATMs
Overall, contactless ATMs offer improved convenience, hygiene, and security, making them an attractive option for users who prioritize these features. But, as is often the case, it doesn’t matter how advanced or necessary a technology is; the implementation process can experience some initial resistance.
While contactless ATMs offer numerous advantages, there may be reasons why some individuals might be hesitant or prefer not to use them (at least for now). Here are some potential drawbacks or concerns associated with contactless ATMs:
Limited Availability
Contactless ATMs may not be as widely available as traditional ATMs, especially in rural areas or regions with less developed banking infrastructure. Users might have difficulty finding one when needed, forcing them to rely on traditional ATMs.Technological Barriers
Some users, particularly the elderly or those unfamiliar with the technology, may find it challenging to navigate contactless ATMs. The use of smartphones or biometric authentication could be confusing or intimidating for those who are not tech-savvy.Privacy Concerns
Some individuals might be concerned about the privacy implications of using biometric data or smartphone-based authentication. They may worry about the potential misuse of their personal information, as well as data breaches or other threats.Device Dependency
Contactless ATMs typically require a smartphone or other compatible device for authentication. Users without compatible devices, or those with dead batteries, may be unable to access these ATMs, making them less practical in certain situations.Technical Issues
Like any technology, contactless ATMs can experience technical problems, such as connectivity issues or software glitches. In such cases, users may not be able to complete their transactions, causing frustration and inconvenience.Perceived Security Risks
Despite the enhanced security features of contactless ATMs, some users may still perceive them as less secure due to their reliance on wireless communication, which they might associate with potential hacking or interception risks.Resistance to Change
Some people may simply prefer the familiarity and routine. As a result, they prefer to keep using traditional ATMs, and are resistant to adopting new technologies.Are Contactless ATMs More or Less Secure?
When you ask the average person how they feel about contactless payments in relation to banking, one of the most common concerns might revolve around security.
To clear some of that up: yes, contactless readers are generally considered more secure than traditional ATMs. That said, this by no means should imply that they are in any way foolproof, either.
Contactless readers, including those used in ATMs and payment terminals, have been designed with security in mind. They employ technologies and measures to mitigate potential fraud and unauthorized transactions. However, no payment system is entirely immune to security threats.
In the next section, we'll elaborate on the security of contactless ATM readers, and discuss potential fraud impacts tied to the machines.
Security Advantages of Contactless ATMs
Some of the security benefits that contactless ATMs bring to the table include:
Encryption & Tokenization
Contactless transactions use encryption and tokenization to protect sensitive data. Each transaction generates a unique, one-time-use code, reducing the risk of intercepted data being reused for fraudulent purposes.Limits on transaction amounts
Contactless payments typically have a maximum limit per transaction, which varies depending on the country or financial institution. This limit helps minimize potential losses in case of unauthorized transactions.Advanced Authentication Methods
Contactless ATMs may use biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition. They may also use smartphone-based authentication. Both of these options are more secure than traditional PIN-based methods.Short-Range Communication
Contactless technology, such as NFC, operates at a short range, making it more difficult for hackers to intercept transaction data.“Zero-Liability” Policies
Many financial institutions have zero-liability policies for unauthorized contactless transactions. These policies protect cardholders from losses resulting from fraud or theft.Security Disadvantages of Contactless ATMs
While the positives probably outweigh the negatives, there are some less-than-secure aspects of contactless ATMs to consider.
Lost or stolen
If a user's contactless card or smartphone is lost or stolen, unauthorized transactions may occur before the user has the chance to report the loss or block the device.Relay Attacks
Although rare, contactless transactions can be vulnerable to relay attacks, where a fraudster captures the transaction data and relays it to another device to make an unauthorized payment.Eavesdropping
While encryption makes it difficult for hackers to intercept and use transaction data, there is still a slight risk of eavesdropping on contactless transactions, potentially leading to data breaches.At the end of the day, contactless readers generally provide a more secure method of conducting transactions due to encryption, tokenization, and advanced authentication methods. However, they are not entirely foolproof.
Users are still vulnerable to contactless payment fraud tactics. They should take necessary precautions to protect their devices and personal information. Merchants and financial institutions, for their part, need a solid risk management strategy in order to limit their overall fraud exposure and protect their bottom line.