Key SaaS Applications That Could Help Maximize Your Revenue
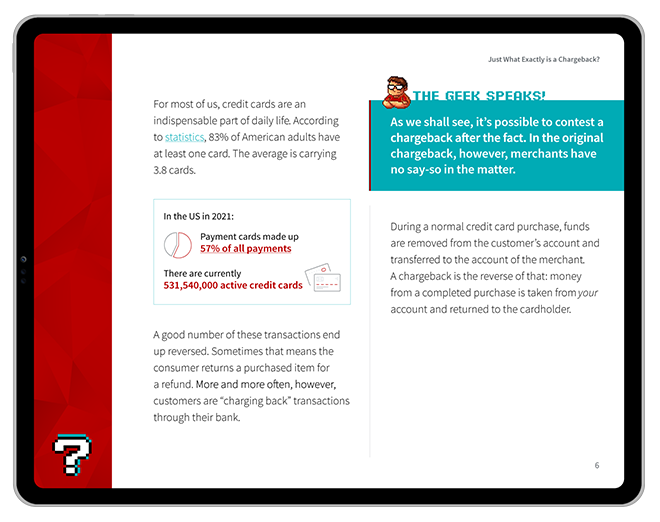
Software as a Service (SaaS) has consistently been the largest and most rapidly expanding market segment over the past three years.
A report from Fortune Business Insights predicts the segment will climb to an impressive $716.52 billion valuation by 2028. Businesses have been ramping up their investments in cloud technologies in response, exhibiting a 20% increase compared to just one year ago.
Furthermore, the reliance on leading SaaS enterprises is steadily growing, indicating these technologies play a crucial role in modern business operations. But, what exactly is SaaS? What constitutes software as a service, and how might it benefit your business most?
Recommended reading
- What is EMV Bypass Cloning? Are Chip Cards Still Secure?
- Dispute Apple Pay Transaction: How Does The Process Work?
- Terminal ID Number (TID): What is it? What Does it Do?
- What is EMV Technology? Definition, Uses, Examples, & More
- Visa Installments: How it Works, Benefits, & Implementation
- dCVV2: How do Cards With Dynamic CVV Codes Work?
What is SaaS?
SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a model of software delivery by which, instead of buying software and installing it on your local machine, you access it via the Internet. The provider hosts the software on the cloud, often based on a subscription model.
“Software as a service” (SaaS) forms one of the three primary aspects of cloud computing, alongside “infrastructure as a service” (IaaS) and “platform as a service” (PaaS). SaaS applications find diverse users, from IT professionals and corporate users to individual consumers.
The breadth of SaaS offerings spans from personal entertainment options like Netflix to sophisticated IT tools. SaaS offerings typically cater to both B2B and B2C markets, making them versatile and widely applicable. This is in contrast to IaaS and PaaS applications, which are primarily business-focused.
Familiar examples of SaaS include Google apps (like Google Docs, Sheets, and Gmail), Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce, Dropbox, and Slack. These tools are all accessed over the Internet and operate under a subscription pricing model.
How Does SaaS Work?
SaaS uses the cloud delivery model.
In this setup, the SaaS provider may use its own infrastructure — servers, databases, and computing resources — to host the application and corresponding data. Or, they may be an independent software vendor (ISV) that leverages a cloud provider's data center for hosting. This means the application becomes accessible to any device with internet connectivity, typically via a web browser.
The beauty of the SaaS model lies in its simplicity for users. Organizations leveraging SaaS solutions are relieved of the burdens associated with software setup and maintenance. They simply pay a subscription fee and gain access to a ready-to-use software solution.
Organizations can integrate SaaS applications with their own software for further customization and functionality using application programming interfaces (APIs). This means a business can create its own software tools and seamlessly integrate them with the SaaS solution through the provider's APIs.
10 Immediate Benefits of SaaS for eCommerce
Software as a Service (SaaS) has transformed the way eCommerce businesses operate, offering a host of advantages that make it an attractive choice for online stores. By leveraging SaaS platforms, businesses can launch and manage their online presence more efficiently and effectively without significant upfront investments or in-depth technical knowledge.
SaaS applications contribute to more streamlined operations, improved customer experience, and enhanced business performance. Some more specific, key benefits that SaaS provides for eCommerce businesses include:
#1 | Ease of Use
SaaS platforms are designed to be user-friendly. Even those with minimal technical skills can typically navigate these systems with ease. This makes it possible for businesses to manage their own eCommerce websites without having to hire a dedicated IT team.
#2 | Cost-Effective
SaaS solutions operate on a subscription basis, usually monthly or yearly, and are more affordable compared to developing a custom eCommerce platform. Additionally, costs are predictable and recurring, making budgeting easier.
#3 | Quick Deployment
SaaS eCommerce platforms are ready-to-use. Businesses can set up their online store quickly without having to worry about the technicalities of hosting, server setup, and software installation.
#4 | Scalability
SaaS platforms are highly scalable. They can handle growth for eCommerce businesses, from small- to large-scale operations, without requiring changes in the system infrastructure. Businesses can adjust their subscription plan to get more resources if the demand increases.
#5 | Automatic Updates
With a SaaS platform, businesses are always using the latest version of the software without needing to update it themselves. The service provider ensures that updates, security patches, and new features are automatically implemented.
#6 | Security
SaaS providers usually offer robust security measures, including SSL certificates for secure transactions, data encryption, and regular security audits. This is important for eCommerce businesses that handle sensitive customer data and financial transactions.
#7 | Integration
Many SaaS eCommerce platforms integrate with a variety of other platforms and services, including payment gateways, shipping providers, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems. This allows for a more streamlined and efficient business process.
#8 | 24/7 Support
Most SaaS providers offer around-the-clock technical support. This means that, if an eCommerce business encounters any issues, help is available at any time.
#9 | Mobile Readiness
As the world is increasingly mobile, having a mobile-friendly site is crucial for an eCommerce business. SaaS platforms often have this capability built-in. Or, it is at least available as an easy addition.
#10 | Future-Proofing
SaaS companies constantly innovate to remain competitive in their respective markets. By partnering with a SaaS provider, your business naturally benefits from these frequent technology and software updates that can keep your business relevant and adaptable.
These benefits emphasize the value of SaaS platforms in helping eCommerce businesses run efficiently and effectively. The key is choosing a SaaS provider that offers the specific features and integrations that align with your unique needs and goals. However, these aren’t the only benefits a SaaS solution offers.
In the next few sections, we’ll discuss key uses for SaaS applications that set the model apart.
SaaS & Data Integrity
In eCommerce, data integrity is paramount. When a business entrusts its data to a SaaS provider, it's not just buying software; it's partnering with a custodian of its data. The role of the provider in maintaining and improving data integrity is multi-faceted.
With the right procedures and technologies, a provider can ensure that a business's data is secure, accurate, consistent, and usable. Here's a closer examination of the various ways SaaS providers uphold and enhance data integrity:
A SaaS provider is responsible for your data integrity and implementing a range of measures to ensure the data's accuracy, consistency, and security. The result is a reliable foundation of data that underpins accurate decision-making and efficient business operations.
SaaS, Security & ID Validation
Identity validation or verification is important to maintaining a secure Software as a Service (SaaS) environment. SaaS providers implement various mechanisms and technologies to verify the identity of users accessing the system, thereby preventing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive data.
Here are some of the ways that SaaS providers use and improve ID validation:
By implementing and continually refining these strategies, SaaS providers work to provide a secure environment that minimizes the risk of fraud while maintaining a smooth user experience.
SaaS & Chargeback Management
Managing chargebacks is vital for maintaining good relationships with customers and preventing financial loss. Every chargeback results in lost revenue. Furthermore, excessive chargebacks can harm a business's reputation and lead to penalties from payment processors.
Here are some ways a SaaS provider can use and improve chargeback management:
Have Additional Questions?
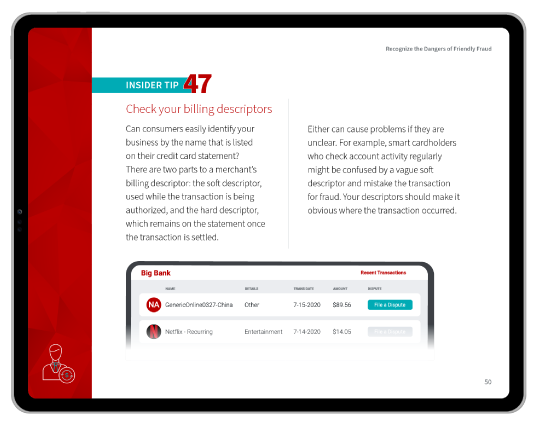
Keep in mind that while SaaS providers can help you greatly reduce the risk of chargebacks, it's virtually impossible to eliminate them entirely. Therefore, a plan to manage chargebacks when they occur is also essential.
Click below to learn more about SaaS chargeback management and why it could be the right choice for your business.
FAQs
What is SaaS?
SaaS, or “software as a service,” is a model of software delivery where instead of buying software and installing it on your local machine, you access it via the Internet. The provider hosts the software on the cloud, often based on a subscription model.
How does SaaS work?
A SaaS provider either uses its own infrastructure— servers, databases, and computing resources— to host the application and corresponding data, or it may be an independent software vendor (ISV) that leverages a cloud provider's data center for hosting. This means the application becomes accessible to any device with internet connectivity, typically via a web browser.
Can SaaS prevent chargebacks?
Nothing can fully prevent chargebacks, but a SaaS solution could improve internal practices and reporting that helps limit the frequency of incoming chargebacks on a monthly basis.