Is Open Banking Equipped to Fight Fraud? The Question Remains Open
We've talked about open banking before, so it might be a familiar topic to some readers already. But, while open banking might be an exciting new frontier in payments, we need to think very hard about whether we're doing everything necessary to counter fraud before jumping in headfirst.
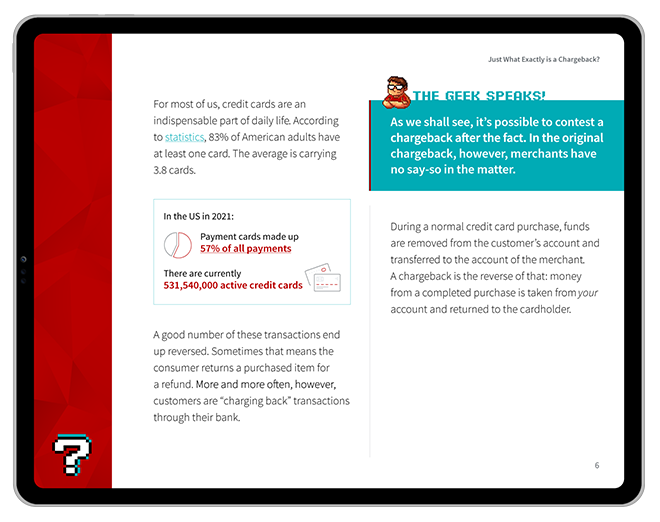
For instance, a recent report from Experian points to a sharp increase in different types of fraud. Deposit and checking account scams, fake identities, and peer-to-peer payment fraud were some of the top threats identified. And, with criminals getting more skilled at using new tech for illegal activities, around 70% of companies have seen an increase in fraud losses in the past few years.
This tells us that fraud is still a big problem. Also, steps need to be taken to deal with it if we're going to see the open banking concept succeed.
Recommended reading
- What is EMV Bypass Cloning? Are Chip Cards Still Secure?
- Dispute Apple Pay Transaction: How Does The Process Work?
- Terminal ID Number (TID): What is it? What Does it Do?
- What is EMV Technology? Definition, Uses, Examples, & More
- Visa Installments: How it Works, Benefits, & Implementation
- dCVV2: How do Cards With Dynamic CVV Codes Work?
Promises of Open Banking
Open banking marks a transformative shift in finance and consumer banking by democratizing access to financial data.
Traditionally held by banks, this data includes transaction histories and spending patterns and can now be securely shared with third-party providers (given customer consent). This change fosters an environment ripe for innovation and competition, breaking down the monopolistic control of traditional banks. The entry of agile, tech-savvy fintech companies into the market promises to revolutionize the creation and delivery of financial products and services.
For consumers, open banking offers a more diverse and personalized range of financial services. They can enjoy the convenience of managing multiple bank accounts through a single app, for instance. They can also access more competitive lending and credit options tailored to their financial behavior. This increase in competition enhances customer choice and improves the overall quality and efficiency of financial services.
Open banking also plays a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion. By using technology to reduce operational costs, it extends financial services to underserved or unbanked populations, particularly in developing regions. This aspect of open banking has the potential to significantly alter the global financial landscape, bringing more people into the formal financial fold.
Despite its benefits, open banking still faces challenges. Namely, there’s the need to establish secure, standardized data-sharing protocols and regulatory frameworks that balance consumer protection with innovation.
Not Enough is Being Done About Fraud
The core of this issue lies in the increased exposure of sensitive consumer data. As financial institutions open their APIs to third-party providers, there is a broadening of the attack surface for cybercriminals. This scenario is not just theoretical; the recent trends in financial fraud indicate a sharp increase in activities exploiting these new vulnerabilities.
For example, the 2023 Fraud and Financial Crime Report underscores the ongoing challenges in managing financial crime risks. This includes the need for transparency and compliance in transactions, particularly in environmental, social and governance (ESG) reporting.
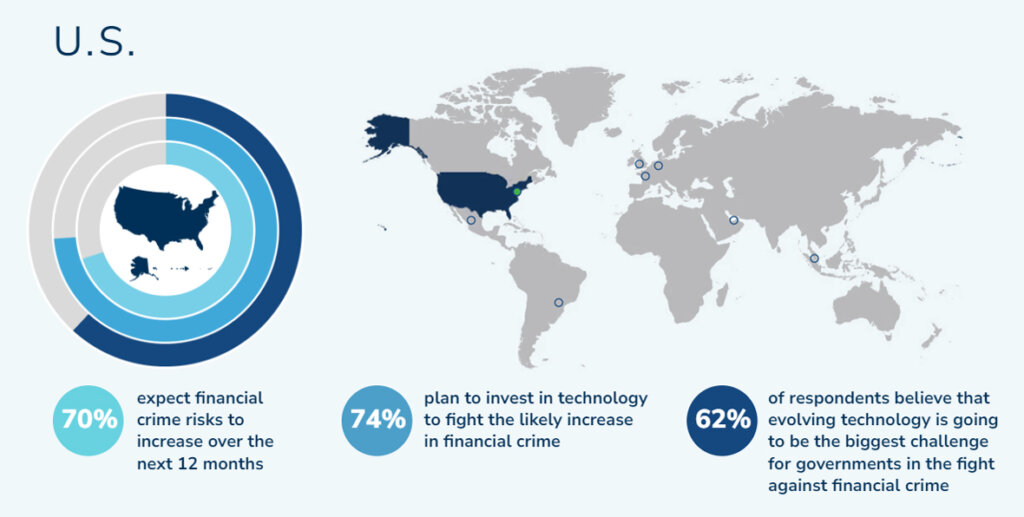
If anything, this data points to an urgent need for a more proactive and data-driven approach to fraud prevention. Traditional reactive measures are proving insufficient in the face of increasingly sophisticated and varied fraud schemes. Financial institutions and third-party providers must leverage advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time monitoring to detect and prevent fraud.
Furthermore, there's a need for more collaboration between financial institutions, technology providers, and regulatory bodies. This collaboration should focus on developing and implementing standardized security protocols and best practices to safeguard sensitive consumer data. Equally important is the need for consumer education, as informed users are a critical line of defense against fraud.

How Banks Can Get Ahead of the Curve
While open banking presents a fertile ground for financial innovation, it also necessitates a heightened and more sophisticated approach to fraud prevention. The financial sector must acknowledge the gaps in current fraud prevention strategies. Firms must invest in more advanced, data-driven solutions to protect consumers and maintain trust in the evolving digital financial ecosystem.
As banks navigate the open banking landscape, they can adopt several strategic measures to enhance fraud prevention and maintain consumer trust. On that note, here are 10 key strategies to consider:
#1 | Advanced Technologies for Fraud Detection
Banks must invest in artificial intelligence and data analytics to enhance their fraud detection capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze transactional data in real time, identifying patterns that indicate fraudulent activity. This proactive approach allows banks to detect and respond to fraud threats more quickly and effectively.
#2 | Improved Cybersecurity Protocols
The security of data transmission is critical in open banking. Banks need to implement stringent cybersecurity measures and ensure that third-party providers comply with these standards. Regular security audits and compliance assessments can help in maintaining high-security standards.
#3 | Collaborative Approach to Information Sharing
Banks should actively participate in industry forums and collaborative networks to share and receive updates on the latest fraud trends. This collective effort enables banks to stay informed and prepare better defenses against emerging fraud techniques (more on this later).
#4 | Comprehensive Customer Education
As mentioned above, informing customers about the risks of fraud and how to protect themselves is highly important. This includes educating them about common scams, the importance of secure passwords, and the perils of sharing sensitive information.
#5 | Continuous Learning & Improvement
Machine learning algorithms, once integrated into fraud detection systems, can continually learn and adapt to new fraudulent tactics. This results in a more dynamic and effective fraud prevention system.
#6 | Regular Compliance & Risk Assessments
Conducting regular assessments and overviews of politics and procedures. This ensures that banks remain compliant with the latest regulatory standards and identify potential areas of risk in their fraud prevention strategies.
#7 | Real-Time Fraud Detection
Implementing systems that monitor transactions in real time makes it possible to identify and mitigate fraud as it happens. This immediate response can significantly reduce the impact of fraudulent activities.
#8 | Cultivating a Security-First Culture
Employees are on the front line in the fight against fraud. Fostering a culture in which every employee is aware and proactive about security can significantly strengthen an institution’s overall fraud prevention strategy.
#9 | Implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication, which means verifying users through multiple redundant channels, adds an extra layer of security. This makes it more challenging for fraudsters to access customer accounts illicitly, while introducing minimal friction to the experience.
#10 | Using Blockchain for Enhanced Security
Blockchain technology is not limited just to cryptocurrency. It can provide a secure and transparent method for verifying identities and validating transactions, reducing the risk of fraud in digital transactions.
By prioritizing security and continuously evolving their fraud prevention strategies, banks can safeguard their operations and further the secure and innovative delivery of financial services in our digital landscape.
Closer Collaboration is Necessary
Closer collaboration between banks is pivotal for the success of the open banking concept, particularly in the area of fraud prevention.
In an environment in which customer data is shared through APIs, collaborative efforts can significantly mitigate the risks of data breaches and fraudulent activities. By sharing information about emerging fraud trends, banks can collectively enhance their understanding and develop more effective strategies to counter these threats.
Working together, banks can also establish and standardize secure data-sharing protocols. This effort improves data security across the board. It also ensures compliance with regulatory standards, which is crucial for maintaining consumer trust in open banking.