Decoding Cash Disbursements for Business: How to Harness Cashflows & Improve Revenue
Every business, big or small, needs a dependable and accurate way to keep tabs on cash disbursements. It’s an integral cog in the machinery of cash flow tracking.
Let's face it, though: wrestling with cash flow and keeping a close eye on cash disbursements can sometimes feel like a serious chore. Out-of-sync accounting can throw a wrench in the works. This leads to lost opportunities, dipping revenues, and fractured relationships with employees and vendors. Left unchecked, the problem could even sound the death knell for your business.
Thankfully, mastering cash disbursement tracking could open up new horizons for your business. It can help you ride the wave of market shifts, craft new offerings, and take your business to the next level.
What is a Cash Disbursement?
- Cash Disbursement
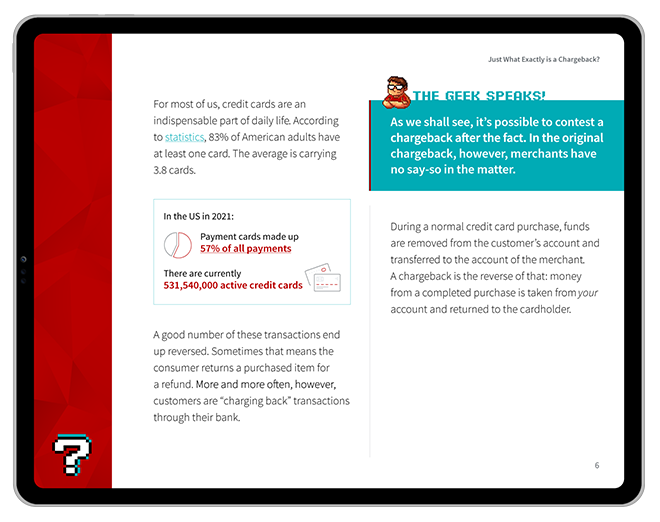
A cash disbursement refers to any distribution of funds in the form of cash. Within the payments sector, it usually implies withdrawals from an ATM or transactions that involve cashback. Such transactions are generally performed using debit cards rather than credit cards, and are often regulated differently compared to regular purchases.
[noun]/kaSH • duhs • burs • mənt/In accounting terms, a cash disbursement represents a payment made from one entity to another. Also known as cash payments, these can be facilitated through checks, electronic checks, Automated Clearing House (ACH), digital payments, and other payment methods that lead to an immediate deduction of funds.
Cash disbursements can be employed for a variety of purposes, including:
- Buying Inventory
- Settling Business Loan Payments
- Covering Accounts Payables & Salaries
- Acquiring Office Supplies
- Paying Dividends
In essence, it covers the execution of any form of payout that doesn't involve a credit account or credit card. Additionally, funds transferred via an intermediary, like an attorney making a payment to a third party on your behalf, can be categorized as a disbursement.
When an employee makes a payment through methods like issuing a check, providing cash, or initiating an ACH or other forms of fund transfers, it is considered a cash disbursement. This payout, in cash or equivalent, is typically documented in a cash disbursement journal (more on this later).
Examples of Cash Disbursements
Cash disbursements are payments a business makes to fulfill its various obligations. These disbursements can be related to various operational, investing, or financing activities. Here are a few examples:
What is a Cash Disbursement Journal?
Essentially, a cash disbursement journal is meant to keep a record of all financial outflows prior to their inclusion in the accounting ledger.
This journal plays a pivotal role in the construction of the organization's general ledger. It’s reconciled with the general monthly ledger entries, forming the basis for the financial statements prepared for each accounting period. Key details recorded in a journal entry usually include:
- Date of Disbursement
- Recipient's Name
- Amount Debited & Credited (Signifying Fund Disbursement)
- Method of Disbursement or Payment
- Reason for the Payment
- Check Number (When Disbursement Involves a Check)
- Any Accompanying Notes
Some businesses may also choose to record additional important specifics, like discounts acquired on bulk purchases. Various expenses may be allocated to different columns or distinguished using unique codes.
Moreover, cash disbursement journals assist in strategic development by offering a comprehensive view of expenditures such as inventory costs, salaries, rent, and other external expenses. Business owners can determine if the company's outflows surpass inflows and vice versa. This will enable strategic adjustments to ensure positive cash flow. In this way, a cash disbursement journal enables more informed decision-making for the mid- to long-term.
It's crucial to note that cash disbursement journals track all forms of cash transactions; not solely physical cash. This includes checks, electronic fund transfers, and any other cashflow streams.
Can You Automate Cash Disbursements?
Of course. Automation exists for those merchants who already feel overwhelmed by accounting processes.
Automating cash disbursements in business accounting can streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve overall efficiency. There are several strategies you can employ to automate this process:
Accounting Software
Many businesses use advanced accounting software packages that offer automation capabilities. These software tools can handle disbursements, generate payments, and update the accounting records automatically.Online Banking
Many banks offer online services that can be used to automate cash disbursements. These services include automatic bill payments and electronic funds transfers, which can be scheduled in advance.Automated Clearing House (ACH)
Merchants can use ACH payments to send money electronically. These payments can be automated, ensuring that bills are paid on time without manual intervention.Integrated Payment Solutions
Merchants can use ACH payments to send money electronically. These payments can be automated, ensuring that bills are paid on time without manual intervention.Outsourcing
Merchants can also consider outsourcing their disbursement processes to a third-party service. These providers have systems in place to handle automated disbursements and can handle the process more efficiently.Remember, before implementing any automated process, it's essential to carefully review and test the system to ensure it's working correctly and securely. After the system is in place, regularly auditing and reconciling disbursements is still necessary to catch and correct any potential errors or issues.
Negative, Delayed, & Controlled Disbursements
Negative disbursement, controlled disbursement, and delayed disbursement are specific cash management techniques. Each is intended to help merchants assume greater control over the disbursement process.
Each of these techniques has its own potential advantages and disadvantages. The right approach can depend on the company's specific circumstances. It's also worth noting that while individual tactics can be useful, maintaining strong overall financial health and cash management practices is often the most important strategy for companies.
Also, remember that the legality and ethical considerations of these practices vary widely. It is important to follow regional regulations and best practices for cash management to ensure fairness and legality in all transactions.
Are Payment Reversals Considered Cash Disbursements?
No. A payment reversal is not typically considered a cash disbursement.
Cash disbursements refer to outgoing payments from a business or an individual to vendors, employees, or other parties as a part of their regular transactions. They involve funds leaving an account and are often associated with the fulfillment of obligations, such as paying for goods or services received, salaries, or debt payments.
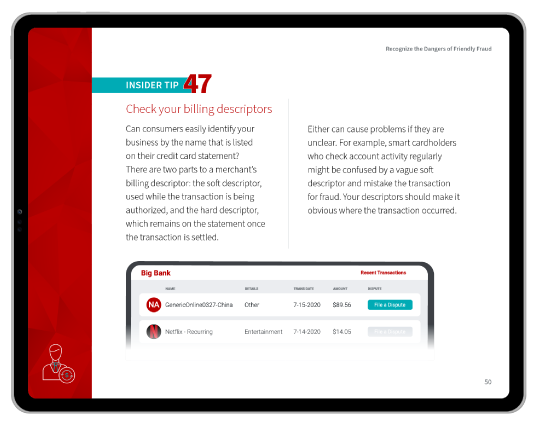
A payment reversal, on the other hand, refers to a situation where funds are returned or credited back to an account. This can occur in several scenarios, such as when a transaction is disputed, an error is found, or a customer returns a purchased item.
“Payment reversal” is a blanket term for any situation in which transaction funds are returned to the cardholder's bank account. Payment reversals are also known as “credit reversals” or a “reversal payment.” Authorization reversals, refunds, and chargebacks are all forms of payment reversals.
There can be situations where a reversal might be seen as a kind of disbursement. For instance, if a business is returning funds to a customer or another business due to an overpayment or a refund. From the business's perspective, this is money going out (similar to a disbursement), and from the recipient's perspective, it's a reversal (money coming in). The terminology depends on the context and the perspective.
But what about other reversals, like chargebacks, for instance?
From the business's perspective, this is an unwanted outflow of cash, similar to a disbursement. But, unlike a regular disbursement, which is typically planned and voluntary, a chargeback is an unplanned and involuntary event.
In accounting terms, while both disbursements and chargebacks involve the outflow of cash, they are usually tracked separately because they are driven by different business activities. Disbursements are part of regular operational expenses. Cargebacks, however, are often tracked as part of a business's loss prevention or risk management activities.
FAQs
What are examples of cash disbursement?
Cash disbursements can include payments for a variety of expenses, such as salaries to employees, payments to suppliers or vendors, rent, utilities, taxes, and more.
Is cash disbursement a payment?
Yes, a cash disbursement is a type of payment. In the context of business and accounting, a cash disbursement refers to any outflow of cash or cash equivalent made by a business.
What are the most common cash disbursements?
Cash disbursements can be made in a variety of ways, including checks, cash, electronic fund transfers, or even debit or credit card payments.
What is the purpose of cash disbursement?
The primary purpose of cash disbursement is to pay off business-related expenses. For instance, paying suppliers, employee wages, etc.