Master Reason Code 4837: No Cardholder Authorization
Chargeback reason code 4837: No Cardholder Authorization applies in situations where customers claim a card transaction was unauthorized, but do not feel the issue can be resolved through the merchant. In such circumstances, networks like Mastercard may allow consumers to reverse such a transaction by filing a chargeback.
To simplify this process, situations that may qualify for a chargeback are broken down into designated “reason codes.” Banks assign the appropriate code to each case so everyone knows the given reason for the chargeback.
We say the given reason because it may or may not reflect the true reason. Merchants must respond to the reason code presented by the bank even if they suspect the cardholder is making an invalid claim, though.
The process is further complicated by the fact that each card network has its own set of reason codes. While most of the same scenarios are covered, the designations can vary considerably. Understanding which code is which can be challenging, so we’ve created guides to help merchants know how best to fight or prevent the different types of disputes.
With that in mind, let’s take a look at Mastercard Chargeback Reason Code 4837: No Cardholder Authorization.
Should Merchants Worry About Reason Code 4837 Chargebacks?
Chargeback questions? We have answers. Click to learn more.

What Is a 4837 Chargeback?
Chargeback reason code 4837 designates disputes involving transactions that customers claim they did not authorize or approve. It is one of four generalized categories into which legitimate fraud-related chargebacks could fall:
- No cardholder authorization (the cardholder simply claims to not have authorized the transaction)
- Questionable merchant activity (the cardholder accuses the merchant of making an error)
- Chip Liability Shift
- Chip Liability Shift Lost/Stolen/Never Received Issue (NRI Fraud)
First, it’s important to understand that this can apply to many different scenarios. Think of chargeback reason code 4837 as an umbrella category; it can be applied to multiple specific situations involving a transaction made without authorization. In every case, though, the cardholder is essentially claiming that the transaction in question resulted from criminal fraud.
When applicable, an additional message will be provided along with the reason code. Financial institutions often refer to this as the Member Message Text. Basically, it tells the merchant which particular chargeback type is the basis of the claim.
Many of the scenarios covered under reason code 4837 had their own specific codes at one time but are now bundled together. Not all disputes require this supplemental information, but many do. Knowing the type of chargeback helps merchants pinpoint the specific reason a point of interaction reason code was used.
Therefore, the Member Message Text could be crucial to understand—and dispute—the specific claim attached to this reason code. The same applies to actions merchants can take to avoid future claims of the same type.
Fraud Disputes: Causes and Conditions
A cardholder filing a claim under reason code 4837 is essentially stating that neither they, nor anyone authorized by them, took part in the disputed transaction. The issuer can also claim that an in-person transaction was made using an account number that is no longer valid.
It's possible that this could be the result of an error on the part of the merchant. It would not fall under the banner of “Questionably merchant activity,” though, as this usually means the merchant is being accused of coercing a customer or taking advantage of a situation. Instead, the source is most likely a fraudster using a lost or stolen card or engaging in account takeover.
If a cardholder claims that a transaction was not authorized, the issuer should then examine the transaction and verify the customer’s claim. The issuer then has a limited timeframe in which to file a chargeback with a “no cardholder authorization” reason code; typically within 120 calendar days of the transaction processing date.
No Authorization Chargebacks and Friendly Fraud
For the most part, legitimate chargebacks resulting from cases of lost or stolen cards are out of the merchant’s control. If a merchant accepts a card purchase from a customer without a valid authorization, they will be held liable for the resulting chargeback.
That said, a growing number of disputes with a 4837 reason code are invalid. “No authorization” is also commonly claimed in cases of friendly fraud, as when the cardholder attempts to force an unearned refund through the bank.
As we noted earlier, the given reason for a chargeback may be completely different from the actual reason. The customer may be experiencing buyer’s remorse or may want to avoid return shipping or restocking fees. Some customers may simply feel that filing a chargeback is easier than following the merchant’s return process. Whatever the true reason, claiming the transaction was never authorized is an easy excuse if one wants to file a chargeback without a valid reason to do so.
Merchants with documentation to support their case have the right to challenge these invalid claims through the representment process.
Preventing Mastercard Reason Code 4837 Chargebacks
If a no-authorization claim is based on merchant activity, there are steps the merchant should take to avoid a recurrence. If the chargeback stems from the use of non-EMV readers, for example, the merchant should implement compliant terminals. Other preventative measures include:
- Using available fraud prevention tools including CVC2, Mastercard SecureCode, and Address Verification Service (AVS).
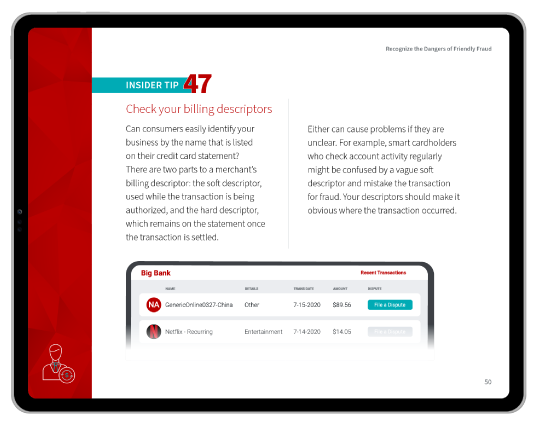
- Ensuring that billing descriptors are easily recognizable.
- Submitting all authorization requests, even for small transaction amounts.
- Designating card-present transactions with an accurate billing descriptor.
- Using the appropriate cardholder verification method (such as PIN).
- Being upfront and fair with customers regarding policies and procedures.
Merchants can take these and many other steps to help prevent legitimate chargeback claims. However, friendly fraud is post-transactional in nature; there’s no sure way to identify it beforehand. Merchants can do everything “right,” but still have suffer customer dispute chargebacks.
It’s generally more efficient to take a proactive stance when it comes to chargeback management. A truly effective strategy, therefore, must focus on both chargeback prevention and disputing cases of friendly fraud.
Chargebacks911® can help your business manage all aspects of chargeback reason codes, with proprietary technologies and experience-based expertise. Contact us today for a free ROI analysis to learn how much more you could save.