What You Should Know About the Adoption of 8-Digit BIN Codes
There was once a time when most phone calls could be made by dialing only 7 digits.
That setup worked fine for an era in which one phone number per household was the norm. But then cell phones happened, and suddenly, the world needed a lot more phone numbers.
We could’ve started making standard phone numbers longer. Instead, the phone companies started increasing the number of area codes, then requiring ten-digit numbers even for local calls.
Why bring this up? Well, we’re about to see something similar happen with credit cards.
In April 2022, the business identification number (BIN) tied to credit cards is going to expand from 6 digits to 8 digits. This time, most consumers won’t even notice the change. That tiny two-digit adjustment could cause major issues for merchants, processors, and financial institutions, though, if they’re not prepared.
In this post, we’ll talk about why we need to transition to 8-digit BINs, and how the change could impact merchants, banks, and customer data security.
Recommended reading
- Merchant Identification Numbers | How Do MIDs Work?
- Why is My Bank Account is Under Investigation?
- Issuer Declines: 7 Reasons They Happen & How to Fix Them
- What is an Issuing Bank? The Issuer's Role in Payments
- What is an Acquiring Bank? The Acquirer's Role in Payments
- How Debit Payment Processing Works: Costs, Rules, & More
Enter the 8-Digit BIN
Although they can range from 8-19 digits, the primary account number for most credit and debit cards is 16 digits long. This is the standard set by the International Organization for Standardization (or ISO).
The 16-digit card number standardized by the ISO won’t change with this update. That means issuers will not have to replace the account numbers of current cardholders.
Instead, the ISO has allowed a format that re-allots two of the existing numbers from another part of the cardholder’s primary account number (or PAN). Two digits that were part of the cardholder’s account identification will be shifted over and added to the BIN code. Here’s what that looks like:
That doesn’t seem like much of a change. The consequences resulting from the 8-digit BIN mandate can still ripple through the entire transaction process, though.
When Will the Transition to 8-Digit BINs Happen?
The ISO first announced this change was coming back in 2015. However, the new 8-digit BIN format wasn’t set to become official until April 2022.
At that point, banks and other FIs can begin issuing cards with 8-digit business identification numbers. Visa has already announced that all newly issued cards will feature Visa 8-digit BINs.
Mastercard 8-digit BIN cards will also be issued after the April launch date. However, the company has not said exactly when it will stop issuing cards with 6-digit codes (as of this writing). Other major networks such as American Express and Discover will likely adopt the new format as well.
Cards with 6-digit BINs will still work after the effective date. However, all merchants and payment processors must be able to support the updated length before that point.
How Will This Impact Merchants?
For many merchants, the new format won’t have much of an impact in the short-term. You’ll obviously need to be compliant with the 8-digit system by the deadline. But, most of the burden of adjusting to the new BINs will fall on acquirers and payment processors.
Expanded BINs are just the latest update to the fintech landscape.
It’s easy to get lost...but we can help you find your way.

There are still exceptions to this. Not all merchants use bank identification numbers the same way. BINs are necessary to make sure payments are matched to issuers. But, they can also be used in other ways, including:
Determining fraud scoring and prevention
Detailed data reporting and analytics
Identifying transactions involved in disputes
Administrating discount and loyalty programs
Validating buyers using geolocation
Those are all optional capabilities, and the majority of merchants don’t rely on them. However, you may have dedicated BIN-based processes that are internally managed. Transaction routing, for example, or fraud reporting. If so, you need to ensure any affected systems are updated to work with the new model.
How 8-digit BINs May Impact Data Security
Credit card data security is monitored and assessed according to PCI-DSS standards. Strict merchant compliance with PCI-DSS standards is necessary to protect card numbers during transactions.
That’s a good thing. Over time, however, various payment processes were designed around this data protection system, based on cards with a 6-digit BIN. Having an 8-digit BIN code may create security risks.
PCI-DSS allows the first six numbers, and last four numbers, of the primary account number to be used in transaction routing. They can also be stored by the merchant with no encryption protocols in place. The merchant can retain some cardholder information, but the full credit card number stays masked.
But, at least for the foreseeable future, both 6-digit and 8-digit BINs will be in use simultaneously. That means merchant and processor systems must be able to process both types of BINs.
The two BIN types can’t always be truncated in the same way. If you’re set up for an 8-digit BIN, but process a 6-digit BIN card, you could be exposing personal cardholder data in the event of a data breach.
Bottom Line:
Applications and processes require more than adaptation for 8-digit BINs. They must also be able to identify which type of BIN is being used.
What Merchants Need to Do
So, what needs to change for you to remain compliant? That varies based on how extensively BINs are used in your processing.
You should start by conducting a comprehensive analysis of your entire organization. Any processing tasks you find that are either dependent on BINs, or internally managed, will likely need to be updated. If you use third-party acquirers or other solutions, it’s important to talk with your provider about compliance with the new system.
Assessing your own business operations can be difficult. You’re probably too close to the situation to remain unbiased. Investing in an independent consultant can more effectively correct potential processing issues before they become security problems.
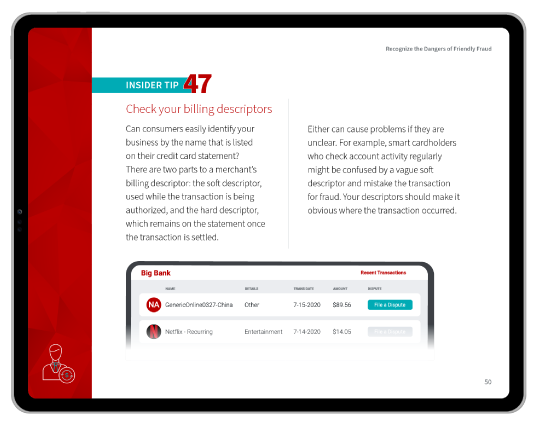
Outside observers can help in other areas, too. Merchant review services from Chargebacks911® will let you identify seemingly minor missteps that could be triggering chargebacks. To learn more, contact us today.