Combatting Buyer’s Remorse: How to Beat the Second-Glance Blues
Have you ever impulsively selected a product for your cart, only to second-guess your decision shortly thereafter? Of course; almost everyone does it.
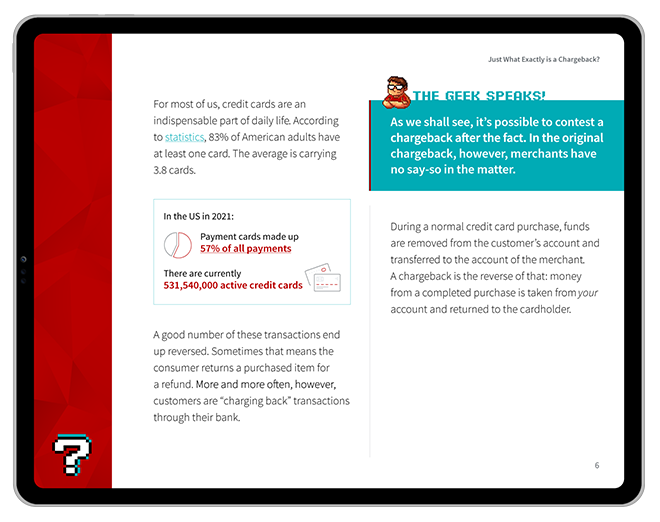
A recent survey by Consumer Reports indicates that nearly 60% of online shoppers have experienced regret after making a purchase. In fact, buyer's remorse is at an all-time high in today's consumer landscape. According to the New York Times, the past year marked a significant rise in instances of buyer's remorse among consumers.
Buyer’s remorse can lead to returns, disputes, and even chargebacks. In turn, this means lower revenue and higher prices for shoppers. That's why it is super important for both businesses and consumers to understand this matter. Also, to know what triggers this behavior, and what proactive steps can be taken to mitigate it.
Recommended reading
- What is First-Party Fraud? Top 5 First-Party Red Flags
- What is Chargeback Fraud? How do You Protect Yourself?
- Return Fraud: What It Is, and How Merchants Can Fight It
- Accidental Friendly Fraud: a Fast-Growing Online Threat
- The Top 10 Tips for Chargeback Fraud Prevention in 2024
- What is “Family Fraud”? How Can You Stop it?
What is Buyer’s Remorse?
- Buyer’s Remorse
Buyer's remorse is a psychological response that arises when a buyer believes they may have made an incorrect or unwise purchasing choice. This often happens when the excitement of a new purchase wears off and is replaced by concerns about its value, necessity, or quality.
[noun]/bī • yərz • rē • mors/Buyer's remorse refers to the feeling of regret or doubt a consumer may experience after making a purchase. This sensation can manifest immediately after the purchase or develop over time as the consumer reflects on their decision.
Buyer's remorse has become increasingly prevalent in today's rapidly evolving consumer landscape. Options are abundant, and purchasing decisions are often made impulsively. That’s especially true online.
The fast-paced nature of eCommerce and the allure of instant gratification has led many to make hasty buying decisions. Later, when the initial excitement fades, they're left questioning whether they truly needed the item or if they received a fair deal. This internal conflict can influence future buying habits and impact businesses' reputations and profitability.
Why Does Buyer’s Remorse Happen?
Unraveling why buyer’s remorse happens is the first step in minimizing its impact and ensuring that customers remain confident in their choices.
Like we mentioned above, buyer’s remorse is a psychological response; like anxiety in response to stress, buyer’s remorse can be triggered by specific experiences. Here are some common triggers that can lead to the onset of buyer's remorse:
The modern consumer's journey is a miniature emotional rollercoaster. A buyer travels from the exhilaration of discovering a new product to the satisfaction of owning their new item — or the potential regret that follows a purchase.
Understanding the psychology behind buying decisions is crucial for businesses aiming to cultivate a loyal and satisfied customer base. It’s also important to understand the real-world impact of this phenomenon.
Consequences of Buyer's Remorse for Businesses
For merchants, buyer's remorse isn't just a fleeting emotion experienced by their customers. It's a substantial force that can shape business outcomes.
When consumers second-guess their purchases, the repercussions ripple out, affecting businesses in some profound ways. Consequences of buyer's remorse for merchants include:
- Increased Returns & Refunds
A surge in returns places a logistical burden on the business. Handling these returns and processing refunds affects not only profitability but also operational efficiency. - Higher Customer Acquisition Costs
Re-engaging a customer who regrets a previous purchase is more challenging. The cost associated with rebuilding trust and confidence often surpasses the initial acquisition cost, stretching marketing budgets. - Damaged Brand Reputation
With the ubiquity of online reviews and social media, a negative post-purchase experience can quickly be broadcast to a wide audience. A single tale of remorse can deter potential customers, weakening the brand's image. - Reduced Customer Loyalty
The foundation of recurring business lies in customer loyalty. An experience marred by regret can erode trust, leading to reduced repeat business and diminishing the lifetime value of a customer. - Lost Sales Opportunities
Customers grappling with post-purchase regret are less likely to engage in additional purchases. This loss extends beyond the immediate sale to potential cross-sells or upsells that might have occurred. - Operational Strain
All backend processes, from customer support to inventory management, feel the strain when addressing the concerns of customers that regret their purchases. The additional resources deployed can impact overall operational efficiency. - Emotional Disconnect
Beyond tangible metrics, there's also the intangible aspect of brand sentiment. A persistent sense of buyer's remorse can create a growing emotional chasm between the brand and its customer base, influencing long-term buying behaviors.
Keep in mind that not every online transaction is just about selling a product. It's also an opportunity to build trust and ensure customers feel good about their purchase.
The customer relationship is defined by give-and-take. Merchants are offering more than just items; they’re also offering confidence (or lack thereof) in the customer experience.
What Can Consumers Do to Curb Buyer’s Remorse?
No one wants to be stuck with a product they didn’t love or really want. That said, as consumers, it’s partially our responsibility to make better-informed choices.
Sometimes, having a shopping list or strategy can help us limit our expenses and improve our relationship with merchants. Here are some other proactive steps that buyers can take to avoid post-purchase regret:
- Do Your Homework
Before making a purchase, spend some time researching the product or service. Read reviews, compare alternatives, and ensure it fits your needs. - Set a Budget
Financial regret is a big part of buyer's remorse. Setting a budget and sticking to it makes you less likely to feel guilt or regret about overspending. - Avoid Impulse Purchases
Give yourself a "cooling-off" period, especially for more expensive items. If you still want the product after a day or two, it's likely a well-considered choice. - Ask for Recommendations
Lean on your network. Friends, family, or colleagues can provide insights based on their own experiences with similar products or services. - Understand Return Policies
Before buying, familiarize yourself with the return policy. Knowing you have the option to return items, and understanding the process and timeframes, can alleviate some apprehension. - Visualize the Product's Place in Your Life
Before purchasing, consider how and when you'll use the product. If you can't envision it fitting into your daily life, then it might not really be necessary to buy it. - Limit External Pressures
Be mindful of sales tactics or peer pressures that might push you to buy something you don't truly want or need. - Check Authenticity
Ensure the authenticity and quality of the product, especially for high-value items. Counterfeit or sub-par items can quickly lead to dissatisfaction.
10 Tips to Help Merchants Prevent Buyer’s Remorse
At the end of the day, the retail experience should be a symbiotic experience. Buyer’s remorse and customer attrition are closely related issues that leave a lot of businesses scratching their heads. But, simply adopting a few best practices can help merchants reach their customers and retain their business.
We should try to keep the relationship as healthy and mutually satisfying as possible. Here are 10 tips to get you started:
#1 | Transparent Product Descriptions
Make sure all product details, specifications, and images are both accurate and comprehensive. The key is to manage and meet customer expectations.
#2 | User Reviews and Testimonials
Facilitate a space for customers to share their experiences. Genuine reviews can offer validation and guide potential buyers in their decision-making process.
#3 | Clear Pricing & Fees
Avoid any last-minute surprises. Ensure all costs, from the product price to shipping fees, are clearly laid out and transparent. Never hide fees in the checkout process.
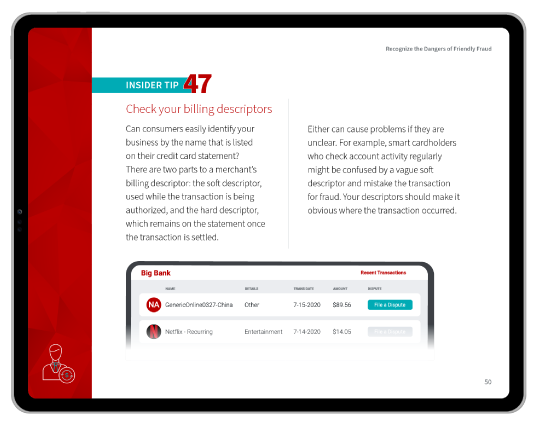
#4 | Flexible Return Policies
By offering an easy-to-navigate return policy, you can reduce purchase hesitations, reassuring customers that they can change their mind if needed.
#5 | Engaging Product Demos
Use videos or interactive demos to give customers a clear understanding of the product. Showing the item from all angles can enhance confidence in the purchase.
#6 | Responsive Customer Service
Equip your support team to address concerns or queries swiftly. A timely response can prevent small doubts from evolving into significant regrets.
#7 | Educational Content
Supplement the shopping experience with guides, FAQs, and tutorials. This aids customers in understanding the product's value and its alignment with their needs.
#8 | Personalized Recommendations
With the help of data analytics, suggest products that align with customer preferences. This ensures a more tailored and resonant shopping experience.
#9 | Post-Purchase Support
Proactively reach out with follow-up communications after a purchase. This reaffirms the buyer’s decision and offers a channel to address any budding concerns.
#10 | Interactive Community Engagement
Foster a community in which customers can discuss products, share experiences, and get advice. This sense of community can be a buffer against potential remorse.
Remember: every step of the customer journey holds profound significance.
As the digital marketplace continues to flourish, it's paramount for merchants to recognize that each transaction extends beyond a mere exchange of product and currency. At its core, it's a testament to trust, understanding, and mutual value.
Merchants must curate each phase of this journey, from the initial product discovery to post-purchase engagements. This is the key to not only limit the shadow of buyer's remorse, but also cultivate an environment where customers feel seen, valued, and consistently satisfied.
In this evolving landscape, prioritizing a seamless and reassuring customer experience isn't just good business. It's the cornerstone of enduring success.
FAQs
How long does buyer’s remorse last?
Buyer's remorse can vary in duration, often lasting from a few hours to several days. However, for more significant purchases, this feeling of regret can linger for weeks or until the issue is resolved, such as through a return or exchange.
What are the symptoms of buyer’s remorse?
Buyer's remorse manifests as feelings of doubt, guilt, or anxiety post-purchase. Affected individuals may obsessively revisit their buying decision, experience discomfort using the purchased item, or harbor a persistent urge to return it. These emotional responses can be intensified, especially if the purchase is substantial or impulsive.
Is buyer’s remorse normal?
Yes. Buyer's remorse is a common psychological response experienced by many consumers after making a purchase. It's a natural reaction to questioning the value or necessity of a recent decision, especially if it involves significant expenditure or commitment.
What is the most common cause of buyer’s remorse?
Buyer's remorse commonly comes up when making impulsive purchases, facing financial concerns after a significant expenditure, or feeling overwhelmed by having too many available choices, leading to doubts about the selected option.
Who is responsible for reducing buyer’s remorse?
Ultimately, the individual experiencing buyer's remorse bears the responsibility for addressing their feelings and decisions. However, merchants can aid the process by offering transparent policies, support, and ensuring clear communication throughout the buying journey.