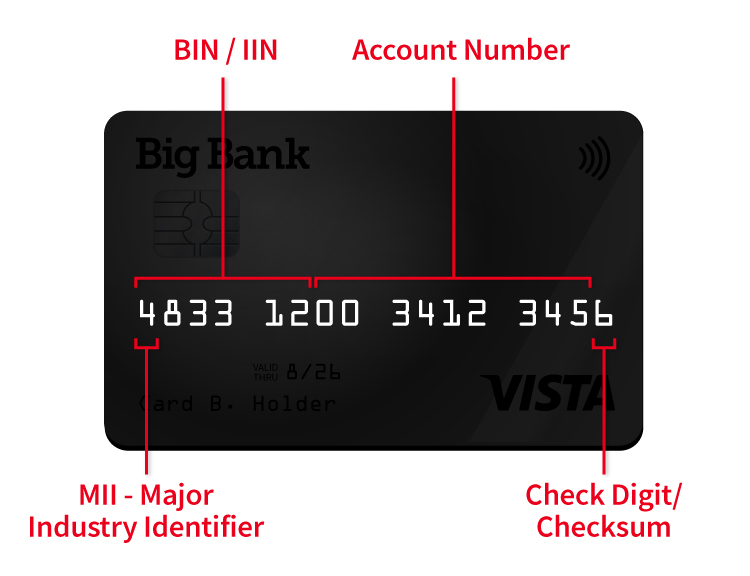
A bank identification number, or BIN, appears as the first four to six digits of a payment method’s card number.
Each BIN is unique and is tied to the bank that issued the card. This means that every credit card, charge card, debit card, prepaid card, and electronic benefit card issued by a particular bank bears the same BIN.
At the top of this page, you can use our BIN number lookup tool and use the credit card identifier system to determine the issuing bank of (almost) any payment card. In the rest of this post, we’ll take a closer look at BINs, how they work, and why they matter.
Recommended reading
- Chargeback Stats: All the Key Dispute Data Points for 2025
- Credit Card Disputes | Step-by-Step Process Guide for 2025
- Mastercard Chargeback Time Limits: The 2025 Guide
- Chargebacks911® Gets in the Game for the Special Olympics!
- Chargebacks911® Food Drive in Support of The Kind Mouse!
- Can You Dispute A Dispute? Yes — Here’s What to Do
What Is a Bank Identification Number?
- Bank Identification Number
A “bank identification number,” or “BIN code,” refers to the initial sequence of four to six numbers that appears on a credit card. The number is used to identify the card’s issuing bank or other financial institution.
[noun]/baNGk • ī • den • tə • fə • kā • SHən • nəm • bər/
All payment cards issued in the United States feature a 15- or 16-digit card number printed on the card face. The bank identification number, or BIN, is the first four- to six- digit sequence in this number.
BINs can help merchants and payment processors identify the bank that issued the card. They can also explain the industry of the issuer, the payment network associated with the card, and the type of card (e.g. credit, debit, prepaid, etc.) being processed.
Recently, some non-bank financial technology companies (e.g. Stripe) have emerged as card issuers. For this reason, the term “issuer identification number,” or “IIN,” is becoming more commonly used. But, both BIN and IIN can be used interchangeably.
What are BINs Used for & Why Do They Matter?
Like we addressed above, bank identification numbers can identify the bank that issued a card. Other, more specific functions include:
What Information Can You Get From A BIN?
Bank identification numbers do far more than just identify the issuing bank.
BINs codes speed up processing and enable merchants to accept multiple forms of payment. When cardholders enter their card details for an online transaction, those first few digits tell the retailer:
- The name, address, and phone number of the bank that funds will be transferred from
- What type of card it is (debit, credit, prepaid, etc.)
- What level the card is (black, platinum, business)
- Whether the issuer is in the same country as the device used in the transaction
- Whether the address provided by the cardholder matches the one on file
The BIN code also helps identify the card brand (Visa, Mastercard, etc.). Here are a few examples of the BIN formats used by the most common card brands in the US:
- Visa: 4*****
- American Express (AMEX): 34**** or 37****
- Diner’s Club: 36****
- MasterCard: 51**** or 55****
- Discover Card: 6011, 622126-622925, 644-649, 65

How are BINs different from Major Industry Identifiers?
A major industry identifier, or MII, is a one-digit number that identifies the industry in which the card issuer operates.
The first digit in every BIN number is the major industry identifier, or MII. This number ranges from 0 to 9 and is used to identify the card network’s “major industry,” based on classifications created by the American Banking Association.
The MII only identifies the industry in which the card issuer operates. For example, issuers assigned an MII of “3” operate in the travel and entertainment industry. Issuers assigned an MII of “4” are in the banking and financial space.
Another difference between BINs and MIIs is that the former is unique; every card issuer has a unique BIN. On the other hand, multiple issuers can share the same MII. For example, all cards branded as a Diners Club card will begin with an MII of 3, regardless of what institution issued the card. This is because the card brand originated as a travel and entertainment card.
Preventing BIN Scams
In a BIN scam, a scammer tries to guess valid account information using brute force methods. If a scammer can guess a valid combination of card details, they will have effectively stolen the associated cardholder’s identity.
Although bank identification numbers are designed to prevent fraud, they can also be used to facilitate unauthorized activity. The most common type of BIN scam occurs when a fraudster starts with an issuer’s BIN and then tries to guess valid account numbers, card verification values, and expiration dates using brute force methods.
A scammer who successfully guesses a valid combination of card details will have effectively stolen the associated cardholder’s identity. The fraudster can then use the victim’s card information to make unauthorized purchases.
BIN attacks, unfortunately, are becoming more common. Fraudsters favor this scam because it’s difficult to trace, but cheap and easy to carry out.
Luckily, fraud prevention tools like 3-D secure authentication and address verification systems (AVS), when implemented properly at checkout, can make card-not-present (CNP) transactions less vulnerable to BIN attacks. The logic is that scammers will have a more difficult time stealing card information when multiple factors of authentication (like billing addresses or one-time SMS-based security codes) are required beyond a card’s verification values.
Learn more about BIN scamsFuture Changes Coming to BIN Numbers
As we discussed above, the term “BIN” itself will most likely give way to IIN eventually. This will happen as new industries enter what has traditionally been banks’ operating environment. That’s not the only change coming to this space, though.
While there’s no shortage of account numbers right now, industry insiders think long-term. In 2016, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) announced changes to the BIN/IIN, including expanding it from six digits to the first 8. As of now, issuers and their processors are not required to move to 8-digit BIN, but they may adopt an 8-digit BIN standard if they choose.
Learn about the 8-digit BIN mandate
Another example of change on this front is the Visa BIN Attribute Sharing Service, or VBASS. This is an optional service that provides merchants and other entities with enhanced Visa BIN data. Use of VBASS helps merchants improve authorization rates, reduce fraud, and improve their overall checkout experience.
Have Additional Questions?
There are additional ways that BINs can be used to help merchants analyze and assess their payment card transactions. More – and more accurate – information can lead to more efficient operations, but the analysis process can be quite involved. That’s why it helps to have professionals in your corner.
If you’d like more information on how to use the bank identification number to your advantage, contact Chargebacks911® today. Our payment experts have the experience and expertise to help you explore different reporting and revenue optimization techniques.
FAQs
How do I find my bank identification number?
You can find your bank identification number on your debit or credit card. The first four to six digits of your card number identifies the bank that issued your payment method.
Is a bank identification number the same as an account number?
No. A bank identification number is a four- to six-digit number that identifies the bank that issued a credit or debit card, while an account number identifies a specific account at the issuing bank.
Is BankID the same as routing number?
No. A BankID, typically known as a bank identification number, appears as the first four to six digits on payment methods issued by a particular bank. BankID may also refer to an eletronic identity verification system in Sweden. A routing number, on the other hand, is a nine-digit number used to identify US banks when sending and receiving ACH and wire transfers.
How do I get my bank identification number?
You can get your bank identification number by taking a look at the first four to six digits of your payment card number. These digits correspond to the specific bank that issued your card.
What is an example of a bank identification code?
A bank identification code, more commonly known as a bank identification number, is a sequence of numbers on a payment card. Bank identification numbers are unique and identify the bank that issued the card.
Are BIC and routing number the same?
No. BICs are used to identify banks when making international transfers, while routing numbers are used by US banks for domestic ACH or wire transfers only.