Defining DRP: How Can Digital Risk Protection Protocols Help You Stay Safe Against Attacks?
Imagine your business as a living organism. Its veins are data streams, its organs are servers, and its lifeblood is the technology that keeps the body dynamic and vital. But, as with any living organism, there are risks and threats that can develop over time.
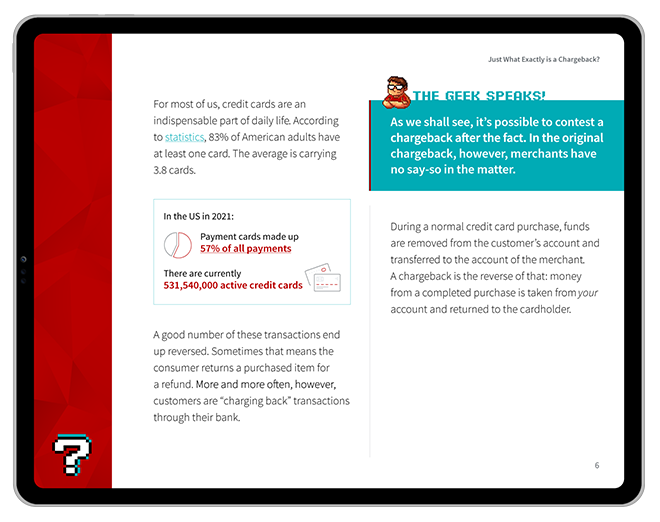
The digital threats you face are growing more sophisticated by the day. Scammers and cyber criminals are keeping pace — and in many, exceeding — the ability of businesses to protect their online ecosystem. This is where digital risk protection, “DRP,” comes into the picture.
Recommended reading
- The Top 10 Fraud Detection Tools You Need to Have in 2025
- Reverse Email Lookup: Tips, Tools & How to Detect Fraud
- ECI Indicators: How to Understand 3DS Response Codes
- Credit Card Fraud Prevention: A Gameplan for Businesses
- eCommerce Fraud Prevention: A Step-by-Step Guide for 2025
- How Device Fingerprinting Works: Use Cases, Trends & More
What is Digital Risk Protection?
- Digital Risk Protection
Digital risk protection (or “DRP”) refers to the set of tools, technologies, strategies, and processes that organizations use to protect their digital footprint from external threats. Examples of DRP operations include social monitoring, digital footprint mapping, and risk assessment.
[noun]/di • jəd • l • risk • prə • tek • SHən/The digital footprint of your company includes all the digital channels in which you have a presence. This spans official websites, social media accounts, cloud services, mobile apps, and more. As you expand, you inherently increase your exposure to digital risks, making DRP an essential aspect of your security posture.
Some of the key aspects of digital risk protection include:
DRP goes beyond traditional perimeter-based and internal network-focused security approaches. It helps provide a comprehensive view of how an organization is exposed to digital threats from all possible angles. This includes external threats that may originate from beyond the organization’s own networks, as well as internal ones.
What Does Digital Risk Protection Entail?
Digital risk protection isn't a “one-size-fits-all” affair. It's a composite strategy made up of four crucial segments that, when combined, yield a comprehensive DRP program. We can call the “The Four M’s” of DRP:
Map
This step involves a thorough mapping of your organization's digital presence to understand where vulnerabilities may exist. For instance, understanding the potential entry points for cyber threats. Assessing your digital assets lays the groundwork for vigilant monitoring of cybercriminal activities.
Monitor
Random, unaggregated data is useless. The monitoring phase turns the ocean of data points at your disposal into a means of developing usable insights. This process encompasses multi-faceted threat analysis, giving context to your digital footprint and keeping tabs on how threats morph over time.
Mitigate
The mitigation phase in digital risk protection is about setting up automated defenses that are both efficient and also broad-reaching. They must empower every department to take a role in risk management, and align with company-wide initiatives to ensure a coordinated defense strategy.
Manage
Managing DRP isn't just about overseeing systems. It involves crafting and implementing comprehensive policies, delving into further threat research, and integrating human intelligence. It also calls for enriching indicators of compromise (IOCs) and sorting through vulnerabilities to identify the most pressing threats.
Digital risk protection and threat intelligence are closely related concepts, but they serve different functions and have distinct focuses. Threat intelligence is information an organization uses to understand the threats that have, will, or are currently targeting the organization. In contrast, DRP pertains specifically to the actions and strategies put in place to protect a company from cyber threats.
DRP systems are designed to sift through and make sense of massive amounts of intelligence data. They ensure security teams can pinpoint threats without being buried under information overload.
These systems can both identify and actively engage with risks. In this way, they provide continuous surveillance and intervention against threats targeting an organization’s digital assets, all in real-time.
Examples of Digital Risk Protection
Now that digital advancements often outpace eCommerce’s ability to secure them, businesses are always on the lookout for faster, more reliable fraud detection solutions. In combination with cyber threat intelligence practices, digital risk protection can transform the way security teams and executives navigate and engage with these threats.
Here's a snapshot of DRP's role in modern cybersecurity:
With DRP as part of the cybersecurity arsenal, your organization can stand guard against the present swarm of cyber threats. You can also craft a future-ready defense, maintaining your digital footprint with confidence and continuity.
8 Essential Benefits of a Multilayer Fraud Prevention Strategy
Digital risk protection practices are a great asset. That said, your business needs several layers of defense to detect, prevent, and respond to fraud in order to avoid financial loss or chargebacks.
At the end of the day, a multilayered approach requires the integration of different tools, practices, and strategies to ensure that all possible vulnerabilities are covered. From digital risk protection to conventional anti-fraud controls, here are eight ways in which this will help you stay safe:
#1 | Countering Diverse Threats
Fraud is complex, and involves multiple channels and techniques. A single defense mechanism may not be adequate to address all the different tactics employed by fraudsters, such as identity theft, phishing, or social engineering. Each layer of defense may target different aspects of fraud, thereby increasing the overall effectiveness of the strategy.
#2 | Defense in Depth
Just as in cybersecurity, the concept of “defense in depth” is critical in fraud prevention. This means having multiple layers of security in place so that, if one layer is breached, others are still in place to prevent or mitigate the damage. This may include technology solutions such as encryption and tokenization, anti-phishing tools, secure payment gateways, and fraud detection algorithms.
#3 | Adapting to Evolving Threats
Fraudsters continually evolve their strategies to bypass security measures. A multilayered approach allows for flexibility and adaptability in fraud prevention tactics. As new threats are identified by AI-enabled intelligence systems, new controls can be put in place to address them without relying on a single solution.
#4 | Comprehensive Monitoring
Layered strategies involve various forms of monitoring, from transaction monitoring to behavior analytics. This helps in the early detection of suspicious activities. You can respond and block potential fraud incidents before they result in chargebacks, reputational damage, or other sources of financial loss.
#5 | Reducing False Positives
A balanced, multilayered strategy can help reduce false positives by cross-referencing alerts from different systems. This approach leads to more accurate fraud detection, improving the customer experience and reducing the loss of sales due to wrongly declined transactions.
#6 | Regulatory Compliance
A layered approach to fraud prevention can help you comply with various regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and other financial industry standards that mandate certain security and privacy controls.
#7 | Combining Multiple Measures
To create a comprehensive fraud prevention strategy, you need conventional security measures, such as customer verification processes, secure handling of physical cards, and checks against fraud databases. However, this must be merged with cybersecurity measures that protect digital assets and data, too.
#8 | xA Holistic Approach
You need a holistic approach to threat management that encompasses both cybersecurity concerns and conventional criminal attacks. By addressing threats comprehensively, you can create a resilient environment in which cybersecurity measures protect against digital risks while conventional fraud prevention techniques deter traditional forms of criminal behavior.
Need help integrating digital risk protection into your fraud prevention strategy? No worries — Chargebacks911® can help. Click below to learn more.
FAQs
What is digital risk protection service?
A digital risk protection (DRP) service is a security solution that identifies, monitors, and manages digital threats across various online channels and platforms. Therefore, any provider, software, or third-party agency that uses this software as a fraud prevention vehicle can be considered a DRP service.
How does digital risk protection work?
Digital risk protection helps guard organizations against cyber threats, data breaches, and other online risks that can affect an organization's assets, reputation, and operations. DRP services provide proactive defense measures, real-time threat intelligence, and rapid response capabilities to secure a company's digital footprint.
Why is digital risk protection important?
Digital risk protection proactively combats a broad spectrum of digital threats that endanger business continuity, customer trust, and compliance with regulatory standards.
What is an example of a digital security risk?
Data leakage is a common source of digital security risk. The illicit extraction and disclosure of sensitive data, whether it pertains to the company or its clients, can be sparked by various triggers, such as business email compromise, account takeover fraud, and spear phishing, for example.